safely operated. The equipment that needs the highest starting wattage are pumps and compressors that start
under load. This equipment can be safely tested. If an overload is detected, the inverters will simply shut down
until the overload situation is corrected. Use the front panel switch to turn OFF the inverter, then ON, to reset
the inverter.
CAUTIONS
Exceeding recommended voltage limits will void manufacturer’s warranty.
NEVER try to use the inverter with any 12 volt DC power source that uses a positive ground. (Most vehicles and
boats use negative ground systems.)
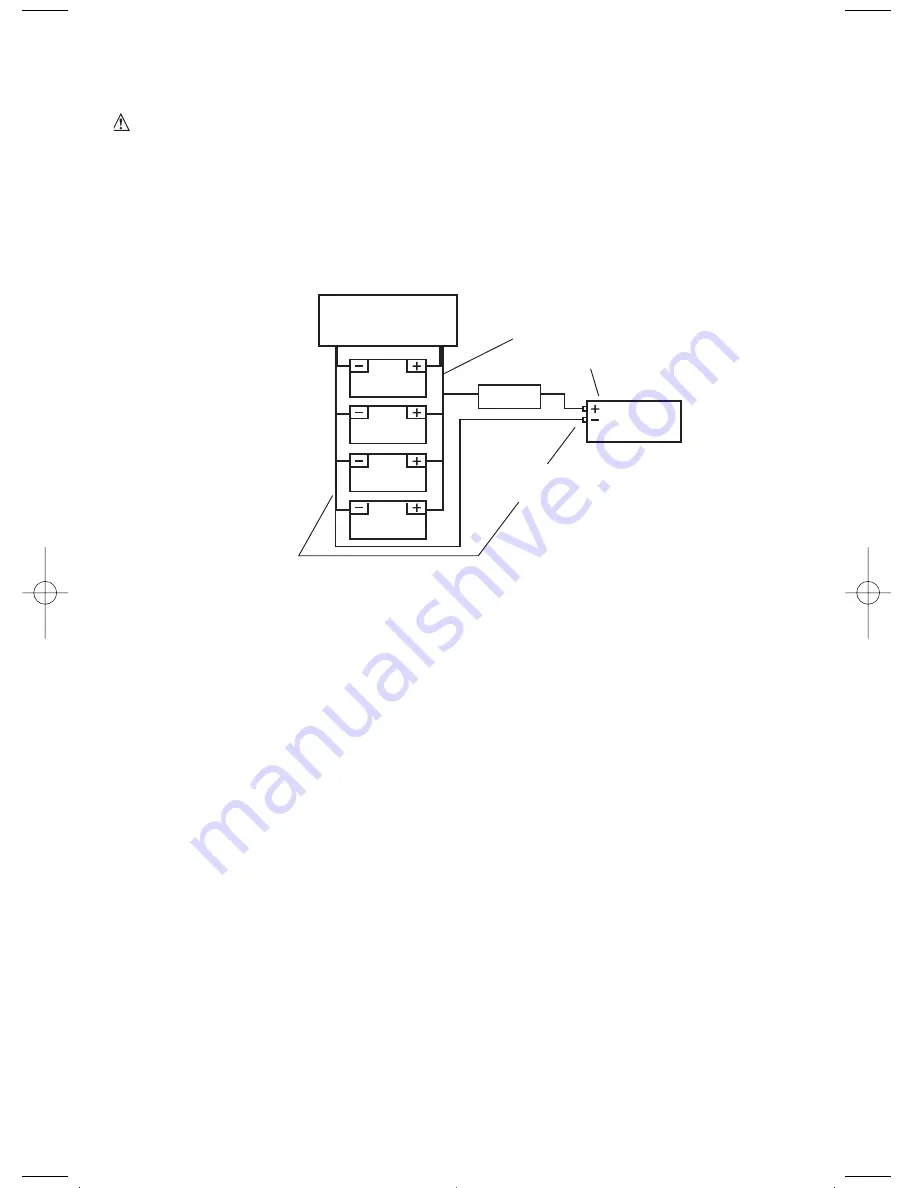
The DC power source must be a well-regulated DC power supply as typically found in vehicle and deep-cycle
marine batteries. The DC power source may also be two 12 volt batteries connected in parallel. On larger
applications the power source may be several batteries connected in parallel as shown in the following “Battery
Wiring” diagram.
Note:
For typical heavy-duty uses, the manufacturer recommends a specified or equivalent ANL fuse be added as
close as possible to the power source (battery) positive terminal. The fuse amperage size must be
appropriate to allow simultaneous operation of all the AC appliances to be powered, with delay
characteristics that allow for the momentary high start-up current requirements of inductive loads. Use the
recommended fuse block (fuse holder) and fuse, or an electrical equivalent. For full rated output and motor
start-up surge output, ensure that the installation is configured to handle the full load. See the
“Specifications” section of this Instruction Manual.
Determining Battery Size
To determine the minimum battery size you will need to operate appliances from MAXX SST™ inverters, follow
these steps:
1. Determine the wattage of each appliance and/or tool you will need to simultaneously operate from the
inverter. To do this, read the labels on the equipment to be operated.
2. Estimate the number of hours the equipment will be in use between battery recharges.
3. Determine the total watt-hours of energy use, the total running time and the average power consumption.
Keep in mind that some appliances are not drawing the same power continuously. For example, a typical home-
use coffee maker draws 500 watts during brew time (approx. 5 minutes), but maintains the pot temperature at
only about 100 watts. Typical use of a microwave is only for a few minutes, sometimes at low power.
Runtime
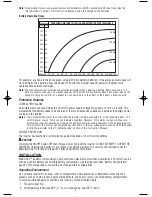
The following graph is a set of curves that show how appliance load, in watts or in amperes, affects runtime.
These curves are only estimates of operating time, dependent upon:
• The condition of the batteries
• The state of charge on the batteries
• The amount of other DC appliances drawing current from the batteries
Three curves were developed for a battery of 50 Ampere Hours (AH) capacity, and three for multiple batteries in
parallel. The higher capacity curves are for 120 AH, 200 aH and 400 aH capacities. These large capacity
batteries clearly extend operating time at full load. To extend operating time in general, reduce the heavy
appliance load to a minimum. Remember, you are operating on stored energy and probably under power loss
conditions.
BATTERY CHARGING
FROM COMMERCIAL
AC, ENGINE,
S
OLAR, ETC.
BATTERY
BATTERY
BATTERY
BATTERY
(MAX FEET OF
AWG WIRE)
(
S
ee the “
S
pecific
a
tions” section)
ANL FU
S
E
FU
S
E HOLDER
(MAX FEET OF
AWG WIRE)
(
S
ee the “
S
pecific
a
tions” section)
FU
S
E TO BATTERY LENGTH
+ FU
S
E TO INVERTER LENGTH
MAXX
SS
T™
POWER
INVERTER
Battery
Configuration
7
VEC054D_ManualEN_092107.qxp 9/24/2007 3:40 PM Page 7