53
Appendix B How to determine where to
set your alarms
1. Oxygen alarms
Two oxygen alarm set points have been provided; one for
low concentrations associated with oxygen deficiencies,
and one for high concentrations associated with oxygen
enrichment.
Oxygen deficiency is the leading cause of worker fatality
during confined space entry. All confined spaces must be
tested for oxygen deficiency before entry. Normal fresh
air contains 20.9 percent O2. Any environment in which
the oxygen concentration is less than 19.5 percent has
been determined by OSHA to be oxygen deficient. The
normal PhD Ultra low-alarm setting for oxygen deficiency
is 19.5 percent.
Common causes of this hazard are bacterial action,
displacement of oxygen by other gases, oxidation
(rusting), consumption (burning), or absorption by
materials such as wet activated carbon.
The PhD Ultra will also alarm for an excess of oxygen.
Too much oxygen in an environment can result in an
increased flammability hazard. The new OSHA
standard for confined space entry (29 CFR 1910.146)
requires that oxygen concentrations not exceed 23.5
percent. The normal setting for the high oxygen alarm is
23.5 percent.
2. Combustible gas alarms
As an environment becomes contaminated with
combustible gases or vapors, concentrations can climb
until they eventually reach ignitable or explosive levels.
The minimum amount of a combustible gas or vapor in
air which will explosively burn if a source of ignition is
present is the Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) concentration.
PhD Ultra combustible gas readings are given in percent
LEL, with a range of zero to one-hundred percent
explosive. The PhD Ultra combustible gas sensor is non-
specific and responds to all combustible gases and
vapors.
Combustible sensors contain two coils of fine wire coated
with a ceramic material to form beads. These two beads
are strung onto the opposite arms of a balanced
Wheatstone Bridge circuit. The "active" bead is
additionally coated with a palladium based material that
allows catalyzed combustion to occur on the surface of
the bead. The palladium catalyst is not consumed in the
combustion reaction, it simply enables it to occur. It is
not necessary for the combustible vapor to be present in
LEL concentrations in order for this reaction to occur.
Even trace amounts of combustible gas present in the air
surrounding the sensor will be catalytically burned on the
surface of the bead.
The "reference" bead lacks the palladium outer coating
but in other respects exactly resembles the active bead.
A voltage is applied across the active and reference
elements, causing them to heat. If combustible vapors
are present, the active bead will be heated by the reaction
to a higher temperature. The temperature of the
untreated reference bead is unaffected by the presence of
gas. The difference between the temperatures of the two
beads will be proportional to the amount of combustible
gas present.
Since the two beads are strung on the opposite arms of a
Wheatstone Bridge electrical circuit, the difference in
temperature between the beads is perceived by the
instrument as a change in electrical resistance.
It is important to note that catalytic "hot bead" type
combustible sensors require the presence of oxygen (at
least 8 - 10 percent by volume) in order to detect
accurately. A combustible sensor in a 100 percent pure
combustible gas or vapor environment will produce a
reading of zero percent LEL.
The amount of heat produced by the combustion of a
particular gas on the active bead will reflect the "Heat of
Combustion" for that gas. Heats of combustion may vary
from one combustible gas to another. For this reason
readings may vary between equivalent concentrations of
different combustible gases.
A combustible gas and vapor reading instrument may be
calibrated to any number of different gases or vapors. If
an instrument is only going to be used for a single type of
gas over and over again, it is usually best to calibrate the
instrument to that particular hazard. If the instrument is
calibrated to a particular gas it will be accurate for that
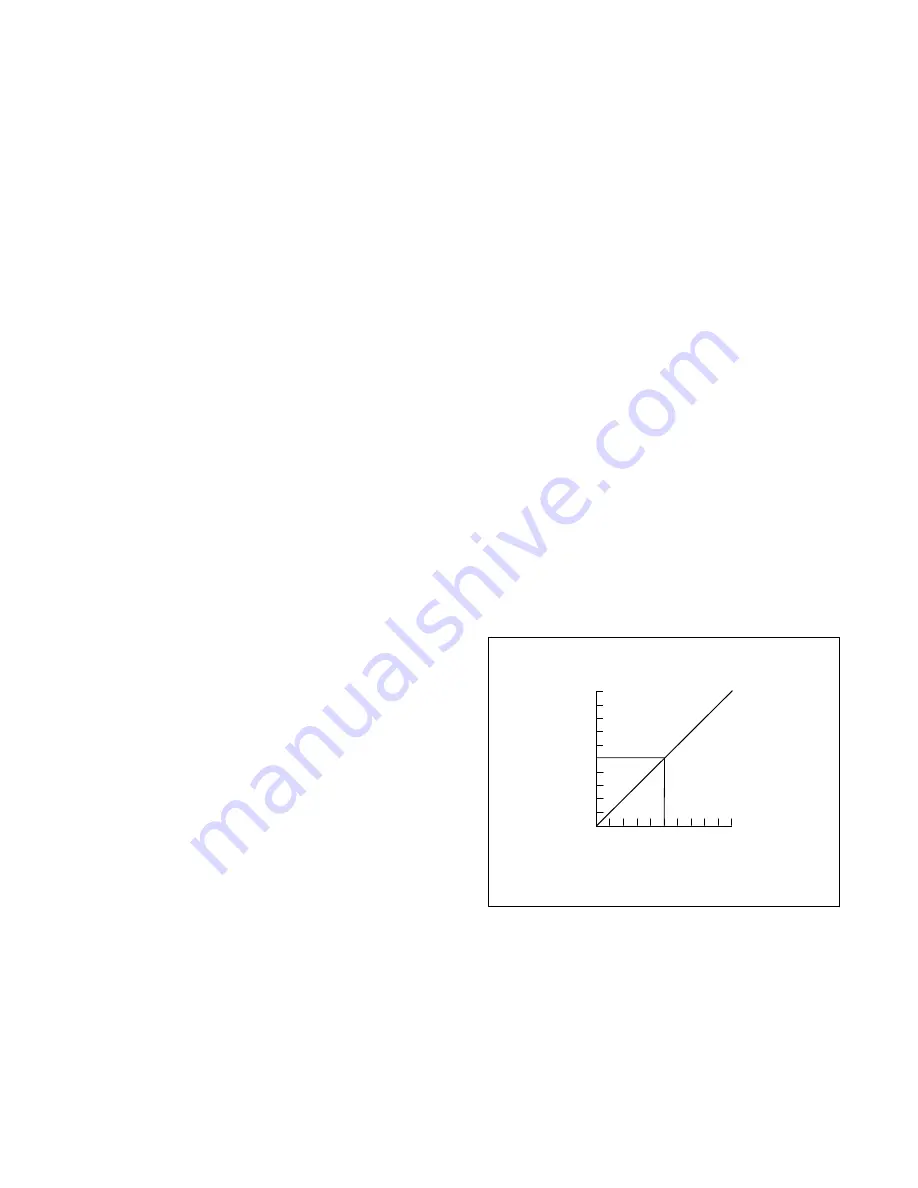
gas. This is what is illustrated in
Figure 2.1.
100
80
60
40
20
20
40
60
80
100
CALIBRATION
STANDARD
ACTUAL LEL CONCENTRATION
RELATIVE
LEL METER
RESPONSE
Figure 2.1. Combustible sensor response to the gas
used to calibrate the sensor
Note that in a properly calibrated instrument, a
concentration of 50 percent LEL produces a meter
response (reading) of 50 percent LEL.
The
Figure 2.2
illustrates what may be seen when a
combustible reading instrument is used to monitor gases
other than the one to which it was calibrated. The chart








































