IN 45 100 010 • AA • 2 / 12
Principle
Ion exchange chromatography (IEX) can be used for purification of biomolecules, such as proteins, peptides and
oligonucleotides, by utilizing the difference in their surface charge. The biomolecules interact with the
immobilized ion exchange groups with opposite charge on the chromatography resin. WorkBeads resins are
available with sulfonate groups (WorkBeads 40S), quaternary amines (WorkBeads 40Q) or tertiary amines
(WorkBeads 40 DEAE) as the ion exchange groups. WorkBeads 40S is a strong cation exchanger and will bind
positively charged molecules. WorkBeads 40Q and WorkBeads 40 DEAE are strong and weak anion exchangers
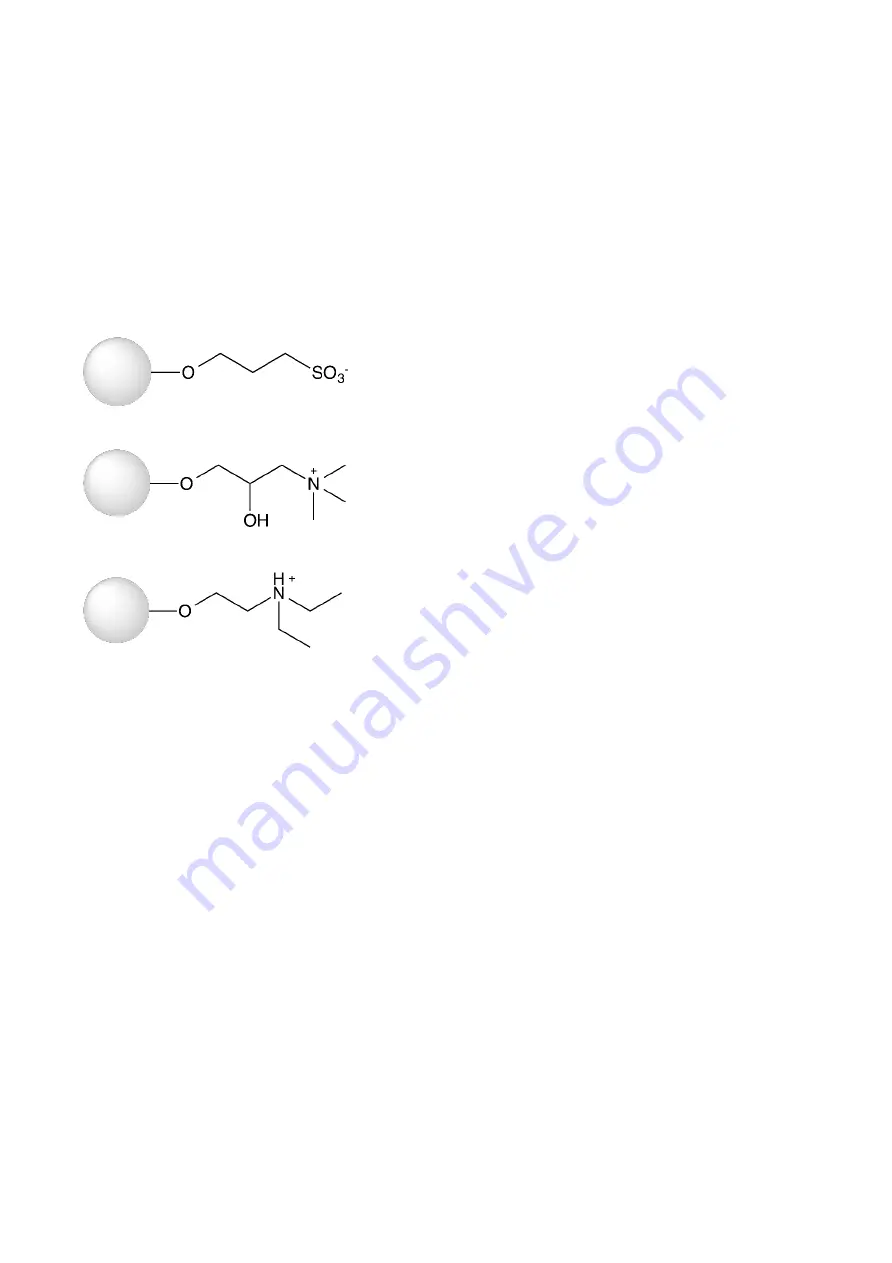
respectively and will bind negatively charged molecules. The structure of the ligands used in WorkBeads 40S,
WorkBeads 40Q and WorkBeads 40 DEAE are shown in Figure 1.
(A)
(B)
(C)
Figure 1. Structure of the ligand used in WorkBeads 40S (A), WorkBeads 40Q (B) and WorkBeads 40 DEAE.
The surface charge of proteins depends on the pH of their environment. When the pH is equal to the isoelectric
point (pI) of the protein the net charge is zero. At pH values below the pI the net charge will be positive, and at
a pH above the pI the net charge will be negative. It should be noted that the interaction of the protein depends
on the presence and distribution of both positive and negative charged groups on the surface (net charge). A
protein may therefore interact with an ion exchange resin also at the pI. The likelihood of binding to either the
cation or the anion exchange resin will increase when moving away from the pI.
Ion exchange chromatography begins with equilibration of the column to establish the desired pH and charging
the resin with suitable counter ions to the charged ligands on the resin (e.g., the negative sulfonate groups can
interact with Na
+
ions and the positive trimethyl amine groups can interact with Cl
-
ions). It is common to use
an equilibration buffer composed of a buffer substance to control the pH, and NaCl to include suitable counter
ions. When the sample is applied, proteins with suitable charge will bind to the charged groups of the resin
while displacing the counter ions. Desorption of the proteins (elution) is carried out by increasing the
concentration of counter ion (salt gradient elution). The counter ions will displace the proteins as the salt
concentration increases. Various additives (e.g., enzyme inhibitors, non-ionic detergents, urea and low
concentrations of organic solvent) can be used in samples and buffers for IEX as long as they do not strongly
interact strongly with the charged groups on the resin or on the protein which could interfere with the protein
binding to the resin.
Ion exchange chromatography is one of the most frequently used chromatography techniques because of its
versatility and ability to separate proteins even with small differences in charge. It is also one of the more cost-
effective chromatography techniques and is therefore excellent for scale-up.