52
11.5.2
Configuration Example
For the three used cameras the following data are known:
Camera
Model
Sensor
Resolution
[Pixel]
Pixel Format
(Pixel Depth)
[bit]
Data
Volume
[bit]
Readout
Time
[msec]
Exposure
Time
[msec]
Transfer
Time
[msec]
LXG-200M.P 5120 x 3840
8
157286400 30.768
6
≈ 73.24
LXG-200M.P 5120 x 3840
8
157286400 30.768
6
≈ 73.24
LXG-200M.P 5120 x 3840
8
157286400 30.768
6
≈ 73.24
▪
The sensor resolution and the readout time (t
readout
) can be found in the respective
Technical Data Sheet (TDS). For the example a full frame resolution is used.
▪
The exposure time (t
exposure
) is manually set to
6
msec.
▪
The resulting data volume is calculated as follows:
Resulting Data Volume = horizontal Pixels × vertical Pixels × Pixel Depth
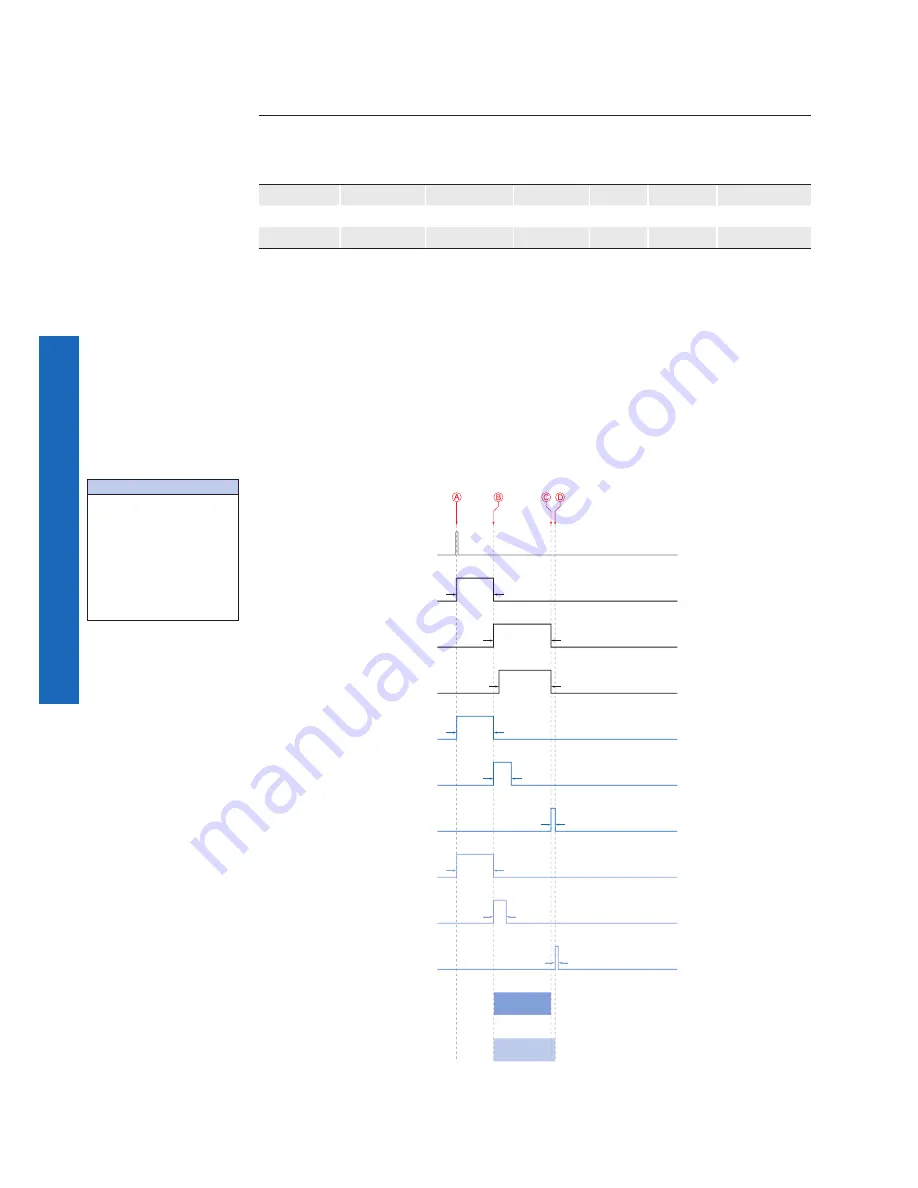
All the cameras are triggered simultaniously.
The transmission delay is realized as a counter, that is started immediately after the sen-
sor readout is started.
Camera 1
(SXG10)
Trigger
Camera 2
(SXG20)
Camera 3
(SXG80)
t
exposure(Camera 1)
t
exposure(Camera 2)
t
exposure(Camera 3)
t
readout(Camera 3)
t
transferGigE(Camera 3)
t
readout(Camera 2)
t
transferGigE(Camera 2)
t
readout(Camera 1)
t
transfer(Camera 1)*
TransmissionDelay
Camera 2
TransmissionDelay
Camera 3
In general, the transmission delay is calculated as:
Timings:
A - exposure start for all
cameras
B - all cameras ready for
transmission
C - transmission start
camera 2
D - transmission start
camera 3
Figure 36 ►
Timing diagram for the
transmission delay of
the three employed
cameras, using even
exposure times.















































