12
Rev. (30-JAN-98) • RLM v4.7
© 1995-98 Automated Logic Corporation
Manually Formatting the Module
Manually formatting the module does not require
communication with the module. Use this procedure as a
last resort when there is no communication with the
module. Although down-loading memory overwrites all
existing memory, it requires communication in order to
initiate the transfer.
WARNING: Formatting the module erases all
transferred memory. The Transferring Memory
procedure must be followed after formatting.
1.
Turn the R683's power switch OFF.
2.
Set all eight of the R683's address and baud rate dip
switches to the ON position (see Figure 1 for
location).
3.
Turn the R683 module's power ON.
4.
Watch the LEDs on the R683 go through the
initialization process.
5.
Turn the R683's power switch OFF.
6.
Set the R683's address and baud rate using the 8-
position dip switch (see Figure 1 for location).
7.
Turn the R683 module's power ON. The module is
now formatted.
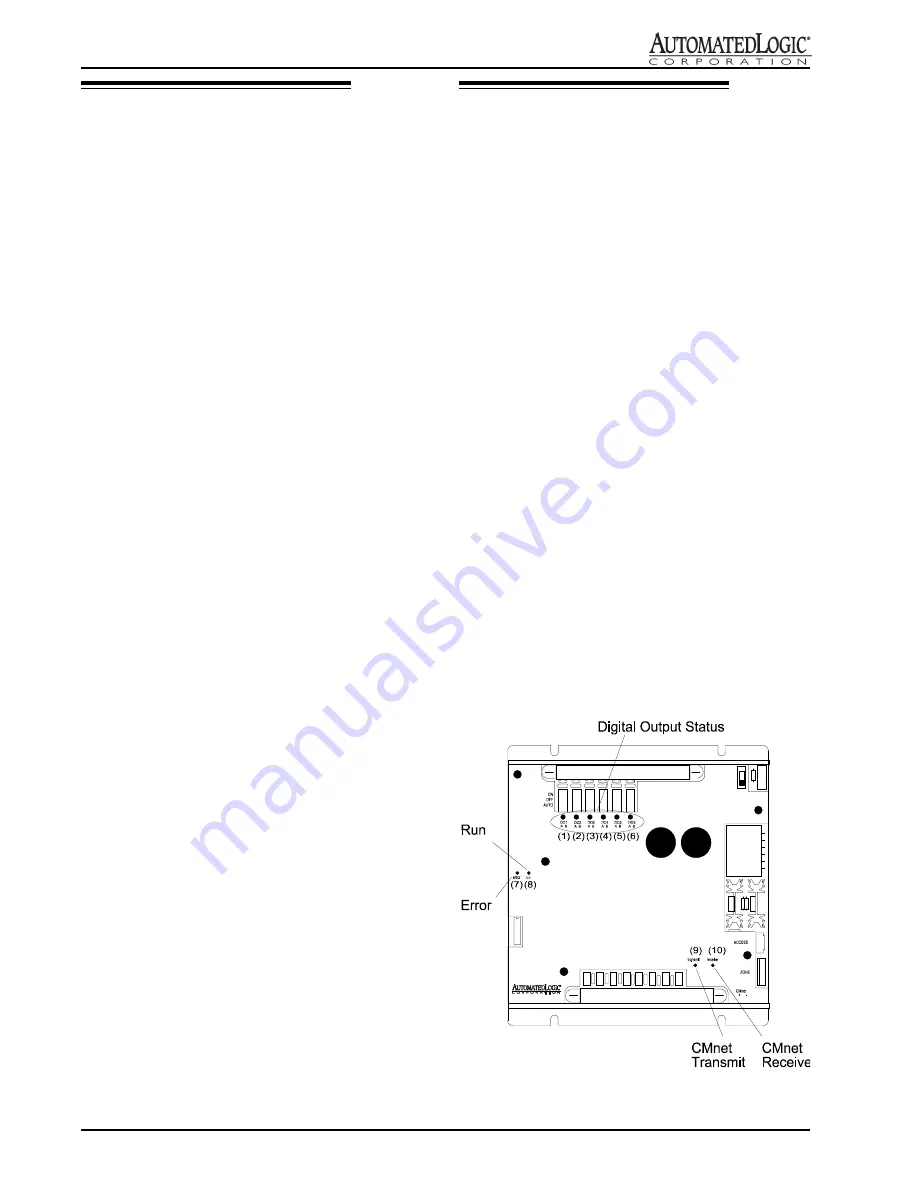
LEDs
Identification
The R683's LEDs are identified as follows (see Figure 16
for location):
Digital Output Status- lights when output is activated.
Error - lights when a software error is detected.
Run - Blinks to indicate R683 is powered and executing
correctly.
Transmit - lights when the R683 transmits data to the
CMnet or access port.
Receive - lights when the R683 receives data through the
CMnet or access port.
LED Power-up Sequence
During power-up, the module goes through an
initialization and self test sequence. Proper module
power-up may be verified by observing the LEDs as the
module is powered ON.
Shortly after power is applied to the module, the
following sequence occurs:
1.
The “Run” and “Error” LEDs will flash.
2.
Both LEDs will pause.
3.
The “Error” LED will turn off.
Figure 16: R683 LEDs
















