V1.0 Vig103M Motherboard Manual
8
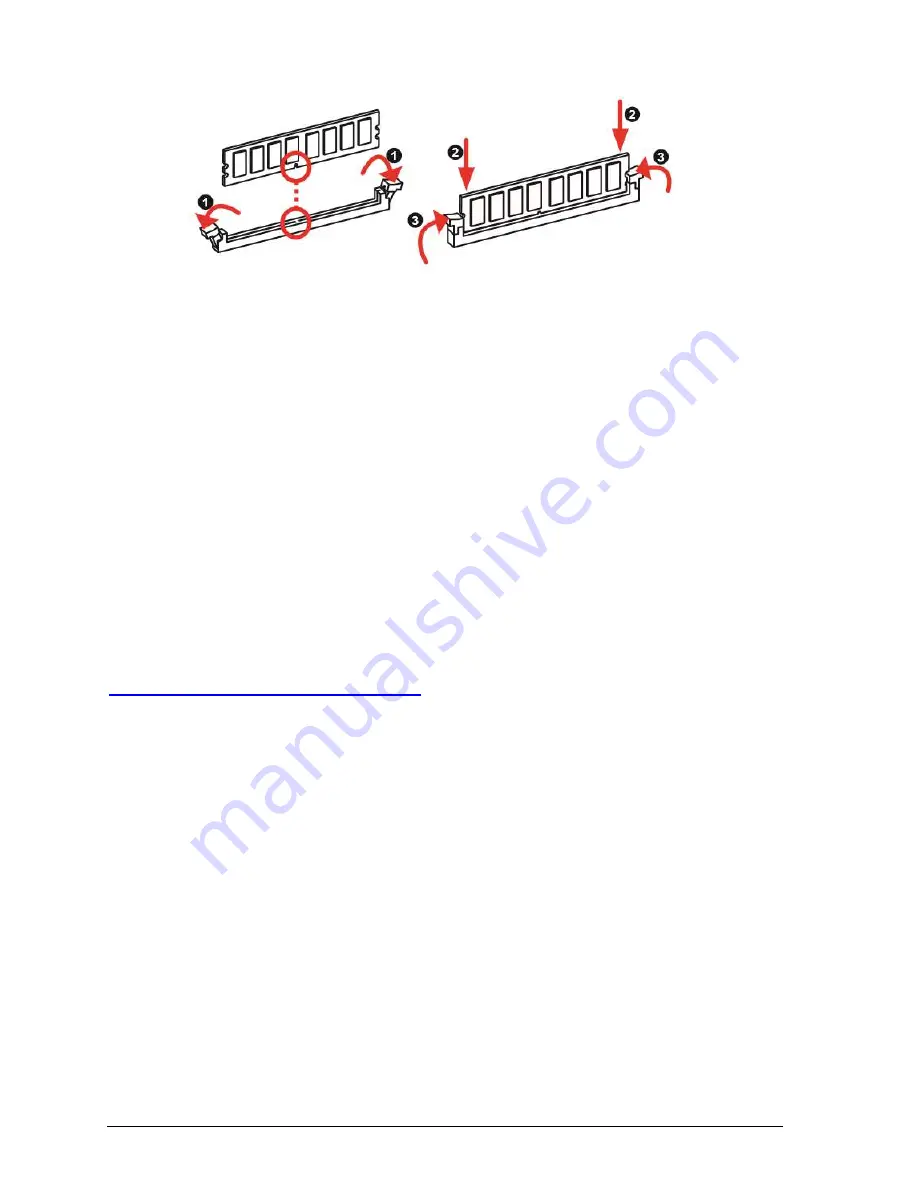
Figure 3:
Memory configuration
NOTE:
To be fully compliant with all applicable DDR SDRAM memory specifications, the board
should be populated with DIMMs that support the Serial Presence Detect (SPD) data structure.
This allows the BIOS to read the SPD data and program the chipset to accurately configure
memory settings for optimum performance. If non-SPD memory is installed, the BIOS will attempt
to correctly configure the memory settings, but performance and reliability may be impacted or
the DIMMs may not function under the determined frequency.
You may install varying memory sizes in DIMM1 and DIMM2. The system maps the total size of
the lower-sized channel for the dual-channel configuration. Any excess memory from the higher-
sized channel is then mapped for single-channel operation.
• According to Intel® CPU spec, DIMM voltage below 1.35V is recommended to protect the CPU.
• Due to the memory address limitation on 32-bit Windows® OS, when you install 4GB or more
memory on the motherboard, the actual usable memory for the OS can be about 3GB or less.
For effective use of memory, we recommend that you do any of the following:
- Use a maximum of 3 GB system memory if you are using a 32-bit Windows® OS.
- Install a 64-bit Windows® OS if you want to install 4GB or more on the motherboard.
For more details, refer to the Microsoft® support site at:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/929605/en-us
.
Memory Configurations
The Intel Core i7, Intel Core i5, Intel Core i3, and Intel Pentium processors support the
following types of memory organization:
Dual channel (Interleaved) mode
.
This mode offers the highest throughput for real world
applications. Dual channel mode is enabled when the installed memory capacities of both
DIMM channels are equal. Technology and device width can vary from one channel to the
other but the installed memory capacity for each channel must be equal. If different DIMM
speeds are used between channels, the slowest memory timing will be used.
Single channel (Asymmetric) mode
.
This mode is equivalent to single channel
bandwidth operation for real world applications. This mode is used when only a single DIMM
is installed or the memory capacities are unequal. Technology and device width can vary
from one channel to the other. If different DIMM speeds are used between channels, the
slowest memory timing will be used.









































