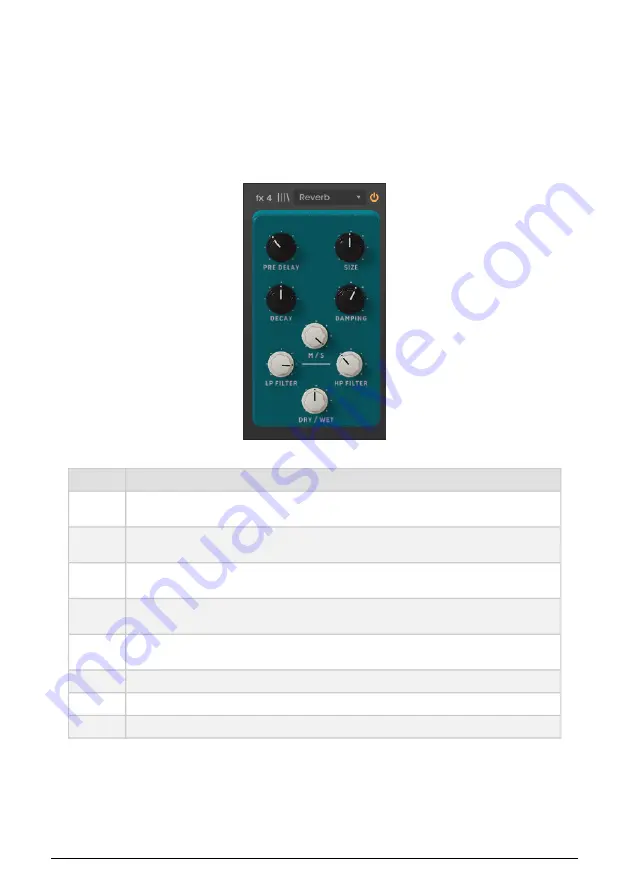
8.2.8. Reverb
Reverberation is the sum of the cross reflections of the audio signal by the different surfaces
of the room or space where the sound source is. It may also be called ambience. The
number of reflections and how they spread and decay defines the type of room (or space)
and its size.
This is an algorithmic reverb, unlike the Room module at the end of the effects chain which
is convolution-based. However, this one can be placed anywhere in the signal chain, so that
other effects can be applied to the sound after it has been processed by the reverb.
Controls
Description
Pre
Delay
Controls the time between the original signal and the first echos (early reflection).
Size
Controls the size of the room or space (basically, the reverb "body"). The bigger the size, the more
reverb that's added.
Decay
Controls the length of the reverb effect (how much time it will last). Should be articulated with the
Damping parameter for a more realistic effect.
Damping
In a room, this parameter defines the absorption coefficient of the reflection surfaces. The higher
the damping the faster the high frequencies will decay.
M/S
Adjusts the stereo wideness of the effect, from mono to an increasingly wide stereo image. Takes
advantage of Mid/Side processing.
LP Filter
Filters the frequencies above the cutoff point, to avoid a sound too harsh.
HP Filter
Filters the frequencies below the cutoff point to avoid too much bass in the sound.
Dry/Wet
Controls the balance between processed and unprocessed sound.
Arturia - User Manual Mellotron V - Mellotron V Effects
68
Summary of Contents for Mellotron V
Page 1: ...USER MANUAL...











































