Currents
Description
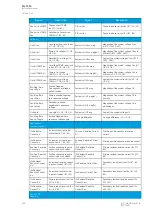
U1 Pos.seq V mag, U2 Neg.seq V
mag
The positive sequence voltage and the negative sequence voltage.
UL1Ang, UL2Ang, UL3Ang,
UL12Ang, UL23Ang, UL31Ang
U0Ang, U0CalcAng
The angles of phase voltages, of phase-to-phase voltages, and of residual voltages.
U1 Pos.seq V Ang, U2 Neg.seq V
Ang
The positive sequence angle and the negative sequence angle.
PPoow
wers
ers
Descrip
Description
tion
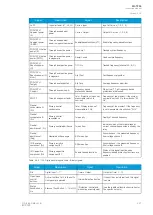
S3PH, P3PH, Q3PH
The three-phase apparent, active and reactive powers.
SL1, SL2, SL3, PL1, PL2, PL3,
QL1, QL2, QL3
The phase apparent, active and reactive powers.
tanfi3PH, tanfiL1, tanfiL2, tanfiL3
The tan (φ) of three-phase powers and phase powers.
cosfi3PH, cosfiL1, cosfiL2, cosfiL3
The cos (φ) of three-phase powers and phase powers.
Impedances and admit
Impedances and admittances
tances
Descrip
Description
tion
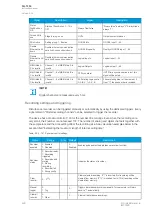
RL12, RL23, RL31
XL12, XL23, XL31,
RL1, RL2, RL3
XL1, XL2, XL3
Z12, Z23, Z31
ZL1, ZL2, ZL3
The phase-to-phase and phase-to-neutral resistances, reactances and impedances.
Z12Ang, Z23Ang, Z31Ang,
ZL1Ang, ZL2Ang, ZL3Ang
The phase-to-phase and phase-to-neutral impedance angles.
Rseq, Xseq, Zseq
RseqAng, XseqAng, ZseqAng
The positive sequence resistance, reactance and impedance values and angles.
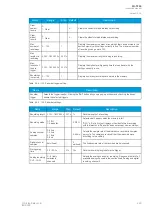
GL1, GL2, GL3, G0
BL1, BL2, BL3, B0
YL1, YL2, YL3, Y0
The conductances, susceptances and admittances.
YL1angle, YL2angle, YL3angle
Y0angle
The admittance angles.
Others
Others
Descrip
Description
tion
System f.
The tracking frequency in use at that moment.
Ref f1
The reference frequency 1.
Ref f2
The reference frequency 2.
M thermal T
The motor thermal temperature.
F thermal T
The feeder thermal temperature.
T thermal T
The transformer thermal temperature.
RTD meas 1…16
The RTD measurement channels 1…16.
Ext RTD meas 1…8
The external RTD measurement channels 1…8 (ADAM module).
Reported values
When triggered, the function holds the recorded values of up to eight channels, as set. In addition to
this tripped stage, the overcurrent fault type and the voltage fault types are reported to SCADA.
A
AQ
Q-T256
-T256
Instruction manual
Version: 2.06
240
© Arcteq Relays Ltd
IM00028
Summary of Contents for AQ-T256
Page 1: ...AQ T256 Transformer protection IED Instruction manual...
Page 2: ......