Addendum
DATA STRUCTURES
Data structures can be defined through software commands to the QCR-Z.
You should have a basic understanding these modes how they affect the
way the QCR-Z scans an image.
Pixel Mode Data
The QCR-Z requires pixel data for each addressable location where its CRT
can display information. If you create images with large amounts of
information and detail, the corresponding image data file will be very large.
Pixel mode is the data structure that sends image data pixel by pixel to the
QCR-Z. An example of the amount of data that would be required for a 4K,
35mm pixel mode image is as follows:
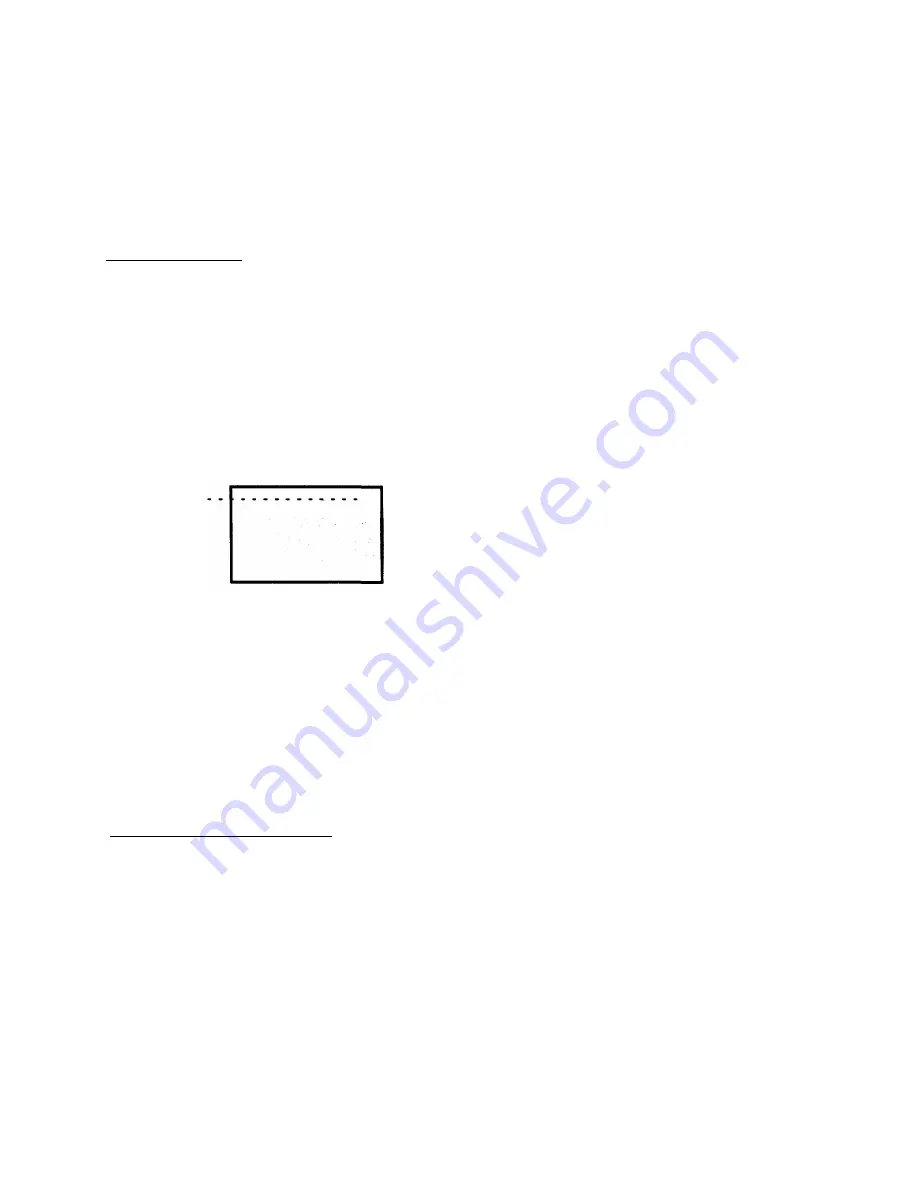
EACH LINE REQUIRES 4096
BYTES OF PIXEL DATA. IF A 35MM
CAMERA OPTION IS USED, 2732
LINES WILL BE PRODUCED FOR
EACH COLOR PASS.
4096 X 2732 = 11,190,272 BYTES
X 3 PASSES = 33,570,816 BYTES
A SINGLE IMAGE WOULD CONTAIN OVER 33 MEGABYTES OF INFORMATION!
Figure A-2. Pixel Mode Data Requirements
Operating The QCR-Z in the 2K mode would decrease the amount of data
by one-half, thereby decreasing the total imaging time, but the image would
also suffer a corresponding loss in detail.
Run Length Encoded Data
Run length encoding is a form of data compression. Groups of pixels can
be defined as segments to reduce the number of data transfers for a given
scan line. RLC can achieve a data compression factor of 90 to 1 or greater.
Simple images such as bar graphs do not require the high resolution detail
that fine art images require, and are ideal for using RLC.
QCR-Z Operator's Guide Version 4
5-4
Summary of Contents for QCR-Z
Page 7: ......
Page 27: ...Installation Figure 3 3 Setting The GPIB Device Address QCR Z Operator s Guide Version 4 3 6 ...
Page 37: ...Operator Instructions Loading Film Into The M120 Module QCR Z Operator s Guide Version 4 4 10 ...
Page 50: ...Addendum Figure A 1 Major Components of the QCR Z 5 3 QCR Z Operator s Guide Version 4 ...
Page 57: ...Addendum This page is intentionally left blank QCR Z Operator s Guide Version 4 5 10 ...







































