Themen
51
Track:
”Track” is the designation for sections on an Audio-CD. This
may be a song, the set of a symphony, etc.
Title/Chapter:
Video-DVDs are divided into “Title” and „Chapters“.
A „Title“ may be e.g. a particular fi lm, the „Chapters“ may be sub-
sections of this fi lm.
Playing media
You transmit commands to the DVD-Player via remote control. It is
thus important to point the end of the remote control towards the
DVD-Player.
1.
Press the remote control button
OPEN/CLOSE
(Fig. 2/19). The
CD/DVD tray opens.
2.
Place the CD/DVD on the tray.
3.
Press the remote control button
OPEN/CLOSE
(Fig. 2/19) again.
The CD/DVD tray closes. The display (Fig. 1/2) fi rst shows „Load“.
After a short while the type of the loaded medium is displayed (e.g.
„DVD“).
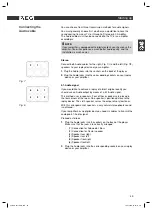
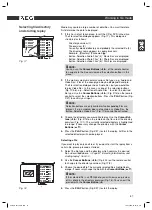
When playing CDs the following status information is displayed on
screen:
Media type (1)
, e.g. “CD”.
Current track/total number of tracks (2).
Audio output (3):
If the
MUTE
-button (Fig. 2/4) on the remote
control was pressed, the audio output is prevented. The word
„MUTE“ appears on the screen.
Repeat (4):
- „x“: no repeat.
- „1“: the current track is repeated.
- „A“: all tracks are repeated.
Specify the repeat with the
REPEAT-
button
➯
Page 54, „Repea-
ting track on CD“
.
Time (5):
This provides information about the duration and the re-
maining play time. By standard the play time expired of the current
track is displayed. The display is in hours, minutes and seconds.
Press the
DISPLAY
-button (Fig. 2/6) once or several times to have
further times displayed.
The following possibilities are available for selection
-
time remaining to the end of the track,
-
expired playing time of the track,
-
time remaining to the end of the CD.
Terminology
Using the remote control
Loading a CD/DVD
Understanding the
onscreen CD-menu
2 / 12
00 :03:09
1
2 3
4
TRK
5
Fig. 11
Playing media
05-DVD 4517 AEG - GB 51
19.01.2006, 10:52:56 Uhr
MPEG-4:
Your DVD-Player is still capable of playing files
compressed in MPEG-4 (short for Moving Picture Experts
Group-4). MPEG-4 is a compression method able to reduce high
amounts of data without a noticeable loss in the quality of
pictures and sound.