1314-900 Revision BA
250W Precision Calorimeter
5
Product Overview
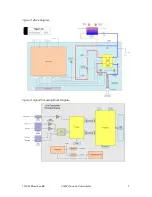
Figure 2: Model 1314 250W Precision Calorimeter (in optional rack w/PC)
The model 1314 is a precision calorimeter that can provide highly accurate RF power
measurements up to 250 W in the 50 Hz to 3 GHz frequency range, and is traceable to the
International System of Units (SI) through the National Institute of Standards and Technology
(NIST) or other recognized National Metrology Institutes, by comparison to equipment and
standards maintained in the laboratories of AE-TEGAM Inc. The calorimeter design is based on
first principles of fundamental physics in the following way. If we know a calorie is a defined as
the amount of energy in the form of heat to raise the temperature of a certain mass of liquid by a
given amount, then conversely, if we know the temperature rise and the mass of the liquid, we
can determine the amount of heat and therefore, the amount of energy applied to the liquid. The
calorimeter utilizes these fundamental relationships to precisely measure input power in the form
of RF energy.
The physics definition of Work is also related to heat by being defined as energy in transition and
work per unit time is power. We can then expand the concept of a calorie to include the rate at
which this heat energy is delivered to the mass of the substance to directly derive power, which
can then be equated to the more useful watt terminology describing our applied RF energy. One
joule (or 1 BTU) of heat equals .239 calories (or 778 ft-lbs) of work, and 1 joule/sec (or 1
BTU/hr) has its electrical equivalent to 1 watt (or .293 W).
Therefore, the fundamental calorimetric relationship between electrical power in watts and the
thermal quantities measured inside the calorimeter are temperature rise ΔT (°C), rate of mass