Section 14
Logic
About this chapter
This chapter describes primarily tripping and trip logic functions. The way the
functions work, their setting parameters, function blocks, input and output signals and
technical data are included for each function.
14.1
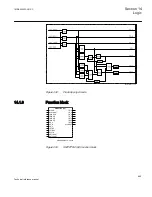
Tripping logic SMPPTRC (94)
Function description
IEC 61850
identification
IEC 60617
identification
ANSI/IEEE C37.2
device number
Tripping logic
SMPPTRC
I->O
SYMBOL-K V1 EN
94
14.1.1
Introduction
A function block for protection tripping is provided for each circuit breaker involved in
the tripping of the fault. It provides a settable pulse prolongation to ensure a trip pulse
of sufficient length, as well as all functionality necessary for correct co-operation with
autoreclosing functions.
The trip function block also includes a settable latch functionality for evolving faults
and breaker lock-out.
14.1.2
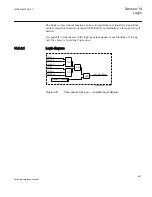
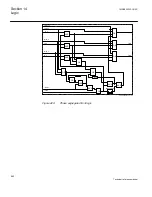
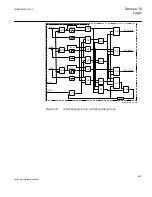
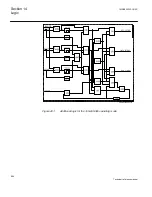
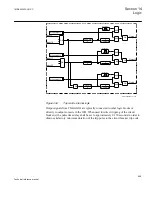
Principle of operation
The duration of a trip output signal from tripping logic common 3-phase output
SMPPTRC (94) is settable (
tTripMin
). The pulse length should be long enough to
secure the breaker opening.
For three-pole tripping logic common 3-phase output, SMPPTRC (94) has a single
input (TRINP_3P) through which all trip output signals from the protection functions
within the IED, or from external protection functions via one or more of the IEDs
binary inputs, are routed. It has a single trip output (TRIP) for connection to one or
1MRK505222-UUS C
Section 14
Logic
859
Technical reference manual
Summary of Contents for Relion 670 series
Page 1: ...Relion 670 series Line differential protection RED670 ANSI Technical reference manual...
Page 2: ......
Page 40: ...34...
Page 50: ...44...
Page 60: ...54...
Page 126: ...120...
Page 384: ...378...
Page 496: ...490...
Page 556: ...550...
Page 602: ...596...
Page 620: ...614...
Page 794: ...788...
Page 864: ...858...
Page 988: ...982...
Page 998: ...992...
Page 1084: ...1078...
Page 1164: ...1158...
Page 1168: ...1162...
Page 1220: ...1214...
Page 1230: ...1224...
Page 1231: ...1225...