IB
6.1.12.1-1C
1
2
ABB
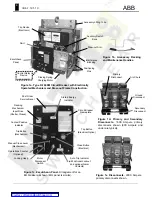
motor is unavailable. Engage the handle with the drive
carrier as demonstrated in Figure 2. Charge springs
by ratcheting the carrier with a smooth, deliberate
motion. Charge until a latching sound is heard as the
closing springs snap over-center. At this point, the
carrier no longer engages teeth of the driven gear and
the stored energy indicator will display “SPRINGS
CHARGED”.
The loaded action of the drive carrier occasionally
back-drives the motor crank arm into a position that
holds the carrier at partial stroke. The crank arm must
be physically rotated to allow the carrier to cycle and
engage the next tooth of the charging gear. With
Ametek motors, this can be accomplished by forcing
the carrier upward against the resistance of the motor
gearing. Because of the higher gearing torque of the
Ryobi charging motor, resetting the carrier is most
easily accomplished by rotating the motor armature.
DANGER
The motor must be isolated from control power before
attempting to turn the armature. Beware of a hot commutator if
the motor was just operated. Do the following:
•
Rack the circuit breaker to the DISCONNECTED position
to isolate it from the control circuit. (Stationary breakers
must have the control circuit de-energized).
•
Wearing a glove (measure of safety), rotate the armature
by turning it at the exposed commutator.
Manually Operated Mechanism
Circuit breakers with a MO mechanism are operated
with the T-shaped closing handle. The mechanism
closes the breaker independent of handle operating
speed. In one operation, the closing springs both
charge and then discharge to close the breaker
without an intermediate stored energy condition.
Manually operated mechanisms therefore do not have
a close control circuit, close latching, or an automatic
spring discharge feature.
Closing Operation
Electrically Operated Mechanism
The energy of discharged closing springs drives the
breaker mechanism to close the breaker contacts.
Closure is initiated locally at the escutcheon panel or
remotely by electrical means.
Standard equipment allows closing at the escutcheon
panel using either the mechanical close lever or the
electrical push button close. The close button
actuates the release (close) coil in the control relay
device. Remote closure uses the same release coil
circuit.
Manually Operated Mechanism
Manually operated breakers are closed at the end of
the charging cycle during the continuous handle
motion described in the charging section.
Opening Operation
The loaded contact springs and two charged opening
springs provide the energy for opening the circuit
breaker. Opening is either manual or automatic.
Manual opening is performed locally with the
mechanical push button trip or the optional push
button electric trip. The push button electric trip
actuates the shunt trip device. Remote opening uses
the same shunt trip circuit. Automatic tripping is
initiated with an overcurrent or undervoltage device.
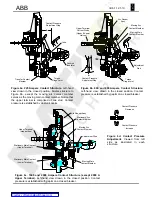
As visualized in Figure 8, depending on the mode of
circuit breaker opening, the secondary trip latch
operates either independently or dependently with
the tripper bar. Shunt tripping and mechanical push
button tripping operate the latch directly without
using the tripper bar. Overcurrent and undervoltage
devices actuate the tripper bar, which in turn rotates
the secondary trip latch. This distinction
discriminates between an intentional opening and an
automatic trip event because the tripper bar also
actuates the automatic trip indicator.
Slow-close Procedure
The purpose of the slow-close procedure is for
checking the travel of the contact assemblies and
adjusting the simultaneous-make between poles.
WARNING
The circuit breaker should be clamped down during the slow-
close procedure to keep it from tilting while manually charging
the closing springs.
Electrically Operated Mechanism
CAUTION
The charging cranks must be reset after the last slow-close
operation or future electrical operation will be impossible (see
steps #8, #9 and #10 below).
1. Charge the closing springs electrically or manually
and observe the closing spring charge indicator.
Turn off the motor disconnect switch.
2. Referencing Figure 3, insert a screwdriver through
the hole in the escutcheon box and depress the
close block pin lever downward.
3. With the close block pin lever held in the down
position, initiate closure with the manual close
lever. Instead of the breaker closing, the spring
load transfers to the close block. The close block
pin lever will remain in the down position.
4. Insert the maintenance handle in the motor drive
carrier as shown in Figure 2. Slowly close the
breaker contacts by actuating the handle.
To repeat the slow-close operation, continue with the
following steps:
5. Re-insert the maintenance handle and complete
the charging cycle until the indicator shows
"SPRlNGS CHARGED" (may already be the case
as in step #4).