Page 25
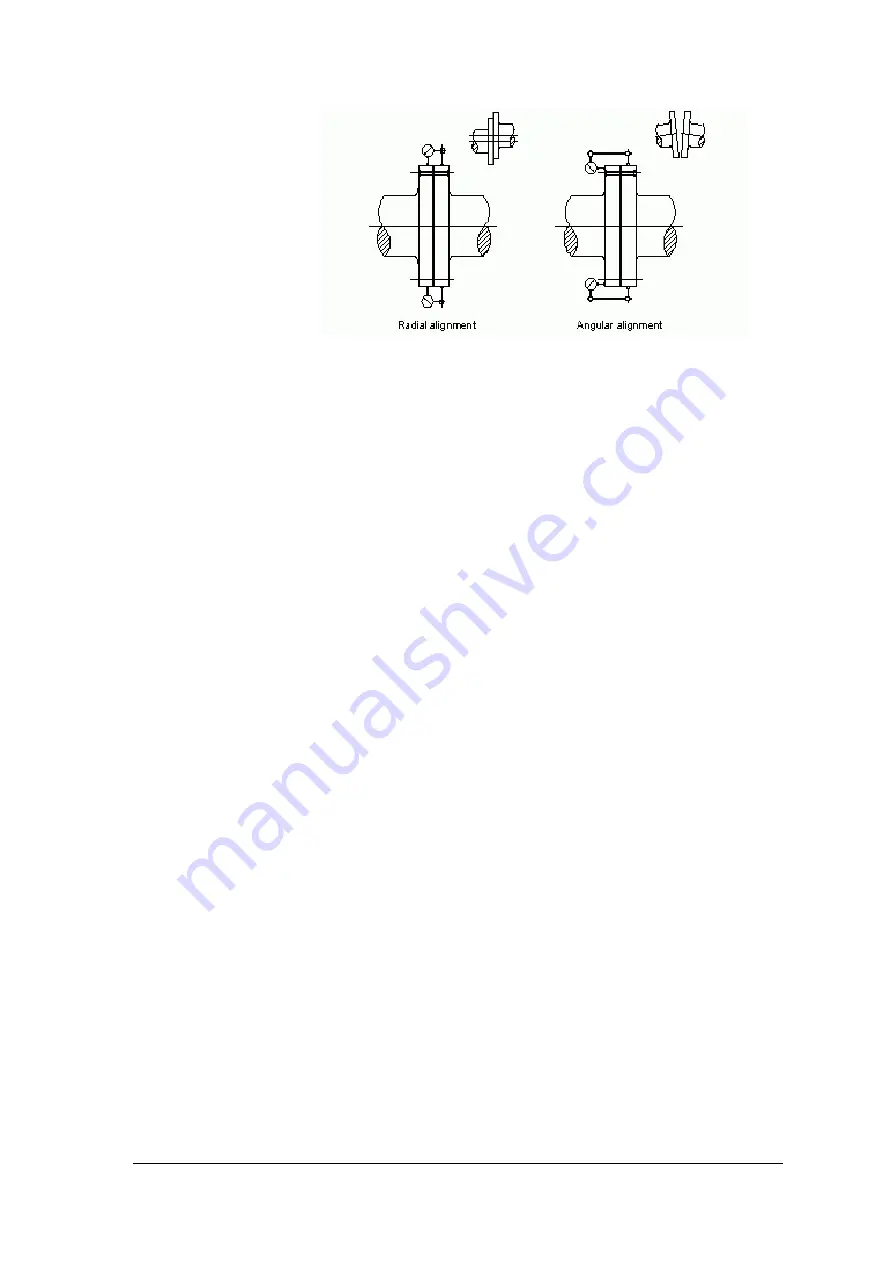
Figure 3-5. Alignment check with gauges
2. Measure and note readings for parallel, angular and axial misalignment in four
different positions: top, bottom, right and left, i.e. every 90°, while both shafts are
turned simultaneously. Record the readings in the
Annex 5.
Commissioning Report
.
3. Align the machine vertically by shimming plates.
•
Tighten the screws of the frame feet.
•
Slacken the rear bottom screws of the prime mover.
•
Tighten the front bottom screws/nuts of the prime mover.
•
Measure the distance between the bottom of the machine feet and the
bed plate and make corresponding solid blocks or wedges or reserve a
necessary of shims.
•
Fit the solid blocks or shims under the generator feet. Tighten the fixing
bolts.
•
Tighten the rear bottom screws of the prime mover, fit solid blocks if
necessary.
•
Tighten the screws to the recommended torque, see
Chapter 7.4.4. The
tightness of fastenings
and check that there is lateral play on the
crankshaft (0.1-0.6mm).
NOTE: During this performance, use torsional spanner for tightening the screws
which connect the flange of the generator and the flywheel housing of
the engine, and the coupling discs and flywheel. For recommended
torques see
Chapter 7.4.4. The tightness of fastenings.
More detailed instructions for installation may be given in instructions supplied
by driven/driving machine manufacturer.
4. Check the alignment again. Make corrections if necessary.
5. Re-tighten the screws. During this performance, use torsional spanner for
tightening the screws. The recommended torques are shown in
Table 7-10.
General tightening torques.
NOTE: The tolerances given by the coupling manufacturers indicate tolerances
for the coupling, not for the driving-driven machine alignment. The
tolerances given by the coupling manufacturer should be used as a
guideline for the alignment only if they are narrower than the maximum
permissible misalignments shown above.
Correction for thermal expansion
















































