ACS510 User’s Manual
135
Start-Up
8119
AUTOCHNG LEVEL
Sets an upper limit, as a percent of output capacity, for the autochange logic. When the output from the PID/PFC
control block exceeds this limit, autochange is prevented. For example, use this parameter to deny autochange when
the Pump-Fan system is operating near maximum capacity.
Autochange Overview
The purpose of the autochange operation is to equalize duty time between multiple motors used in a system. At each
autochange operation:
• A different motor takes a turn connected to the ACS510 output – the speed regulated motor.
• The starting order of the other motors rotates.
The Autochange function requires:
• External switchgear for changing the drive’s output power connections.
• Parameter 8120
INTERLOCKS
= value > 0.
Autochange is performed when:
• The running time since the previous autochange reaches the time set by 8118
AUTOCHNG
INTERV
• The PFC input is below the level set by this parameter, 8119
AUTOCHNG
LEVEL
.
Note!
The ACS510 always coasts to stop when autochange is performed.
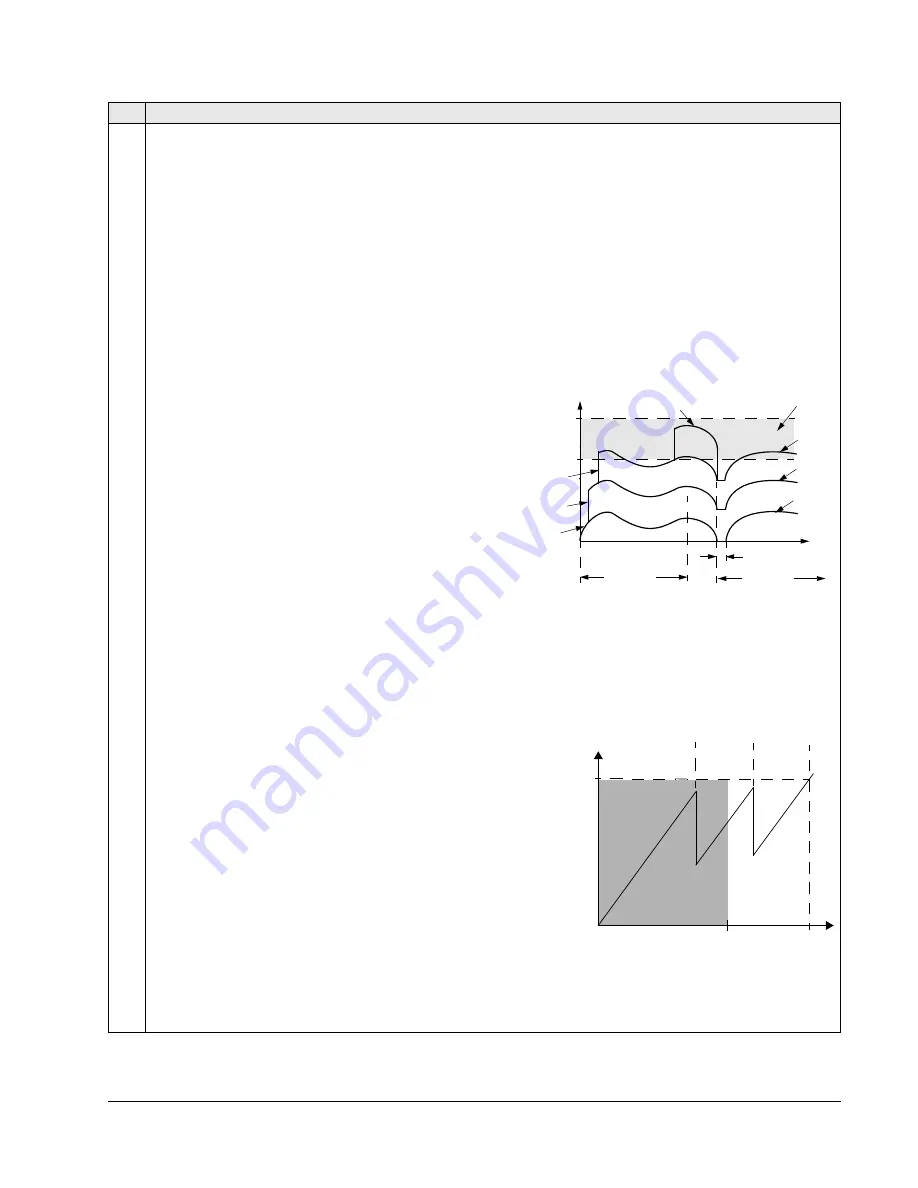
In an autochange, the Autochange function does all of the
following (see figure):
• Initiates a change when the running time, since the last
autochange, reaches 8118
AUTOCHNG
INTERV
, and PFC
input is below limit 8119
AUTOCHNG
LEVEL
.
• Stops the speed regulated motor.
• Switches off the contactor of the speed regulated motor.
• Increments the starting order counter, to change the
starting order for the motors.
• Identifies the next motor in line to be the speed regulated
motor.
• Switches off the above motor’s contactor, if the motor was
running. Any other running motors are not interrupted.
• Switches on the contactor of the new speed regulated
motor. The autochange switchgear connects this motor to
the ACS510 power output.
• Delays motor start for the time 8122
PFC
START
DELA
y.
• Starts the speed regulated motor.
• Identifies the next constant speed motor in the rotation.
• Switches the above motor on, but only if the new speed
regulated motor had been running (as a constant speed
motor) – This step keeps an equal number of motors running before and after autochange.
• Continues with normal PFC operation.
Starting Order Counter
The operation of the starting-order counter:
• The relay output parameter definitions (1401…1403 and
1410…1412)) establish the initial motor sequence. (The lowest
parameter number with a value 31 (
PFC
) identifies the relay
connected to 1PFC, the first motor, and so on.)
• Initially, 1PFC = speed regulated motor, 2PFC = 1st auxiliary
motor, etc.
• The first autochange shifts the sequence to: 2PFC = speed
regulated motor, 3PFC = 1st auxiliary motor, …, 1PFC = last
auxiliary motor.
• The next autochange shifts the sequence again, and so on.
• If the autochange cannot start a needed motor because all
inactive motors are interlocked, the drive displays an alarm
(2015,
PFC
INTERLOCK
).
• When ACS510 power supply is switched off, the counter
preserves the current Autochange rotation positions in permanent memory. When power is restored, the
Autochange rotation starts at the position stored in memory.
• If the PFC relay configuration is changed (or if the PFC enable value is changed), the rotation is reset. (See the first
bullet above.)
Code Description
t
P 8118
B
PID Output
P 8119
100%
P 8118
1PFC
2PFC
3PFC
4PFC
4PFC
2PFC
3PFC
A
P 8122
A = Area above 8119
AUTOCHNG
LEVEL
–
autochange not allowed.
B = Autochange occurs.
1PFC, etc. = PID output associated with each motor.
No aux
1 aux
motor
2 aux
motors
motors
PID output
P 8119
100%
Output
f
MAX
Area
frequency
Autochange
is Allowed
Supplied from China by: Guangzhou Tofee Electro Mechanical Equipment Co., Ltd
Email: [email protected]
















































