XEROX WorkCentre
5735/5740/5745/5755/5765/5775/5790
Information Assurance Disclosure Paper
Ver. 2.00, March 2011
Page
24 of 50
3.2.
Login and Authentication Methods
There are a number of methods for different types of users to be authenticated. In addition, the
connected versions of the product also log into remote servers. A description of these behaviors follows.
3.2.1.
System Administrator Login [All product configurations]
Users must authenticate themselves to the device. To access the User Tools via the Local UI, a numerical
PIN is required. The customer can set the PIN to anywhere from 3 to 31digits in length. This PIN is
stored in the controller NVM and is inaccessible to the user. Xerox strongly recommends that this PIN be
changed from its default value immediately upon product installation. The PIN should be set to a
minimum of 8 characters in length and changed at least once per month. Longer PINs can be changed
less frequently; a 9-digit PIN would be good for a year. The same PIN is used to access the
Administration screens in the Web UI.
3.2.2.
User authentication
Users may authenticate to the device using Kerberos, LDAP, SMB Domain, or NDS authentication
protocols. Once the user is authenticated to the device, the user may proceed to use the Network
Scanning features listed above.
The WebUI allows an SA to set up a default authentication domain and as many as 8 additional
alternate authentication domains. The device will attempt to authenticate the user at each domain
server in turn until authentication is successful, or the list is exhausted.
3.2.2.1.
Kerberos Authentication (Solaris or Windows 2000/Windows 2003)
This is an option that must be enabled on the device, and is used in conjunction with all Network
Scanning features (Scan to File, Scan to E-mail, internet fax, and Scan to Fax Server). The authentication
steps are:
1) A User enters a user name and password at the device in the Local UI. The device sends an
authentication request to the Kerberos Server.
2) The Kerberos Server responds with the encrypted credentials of the user attempting to sign on.
3) The device attempts to decrypt the credentials using the entered password. The user is
authenticated if the credentials can be decrypted.
4) The device then logs onto and queries the LDAP server trying to match an email address against the
user’s Login Name. The user’s email address will be retrieved if the personalization option has been
selected on the Authentication Configuration page.
5) If the LDAP Query is successful, the user’s email address is placed in the From: field. Otherwise, the
user’s login name along with the system domain is used in the From: field.
6) The user may then add recipient addresses by accessing the Address Book on the LDAP server. Please
see the User Manual for details. Each addition is a separate session to the LDAP server.
3.2.2.2.
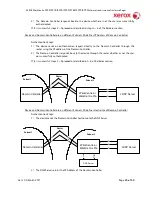
SMB Authentication (Windows NT 4 or Windows 2000/Windows 2003)
This is also an option that may be enabled on the device, and is used in conjunction with all Network
Scanning features (Scan to File, Scan to E-mail, internet fax, and Scan to Fax Server). The authentication
steps vary somewhat, depending on the network configuration. Listed below are 3 network
configurations and the authentication steps.
Basic Network Configuration: Device and Domain Controller are on the same Subnet
Authentication Steps:
1)
The device broadcasts an authentication request that is answered by the Domain Controller.