GLOSSARY OF TERMS FOR GUI
GUI (Graphical User Interface): A graphics-based operating system interface that uses icons
and menus to manage interaction with the system.
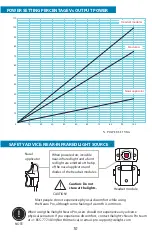
Power: The output power can be adjusted for the individual modules from 1 to 100 %. This
can be translated to mW/cm2 by using the table on page 9.
Power sweep: This feature allows the user to vary the power over the course of a run. The
user can set the start and end power, with stated increments over time.
Power lock: During the course of a run with power sweep, the user can stop the power
increment and hence locking the power value until the end of the run.
between 1 and 10,000 Hz.
Frequency sweep: This is a feature that allows the user to set the start and end frequency,
with selected incremental frequency intervals over the run time.
Frequency lock: During the course of a run with frequency sweep, the user can stop the
sweep, which will lock the frequency value until the end of the run.
Phase: There are 2 frequency phases (A & B) that can be set for each output module. Phase
A is anti-phased to phase B in the default setting.
module. The 50% setting will cause the module switch ON and OFF at 50% of each cycle.
The ON setting will cause the module to be switched on continuously over the course of
the run period.
Time: The run start and stop time can be set for each output module. A delay to the start
can also be set. The delay and active time will be the total activity time for the module,
sweep is active, the total activity time is determined by the start and end values.
Module: There are 8 hardware output modules, and they are pre-listed in each setting
Module control: “Module control” is a tab where the user can access setting for phase and
Group setting: Single runs can be grouped to run concurrently, making it a group setting.
simulated run, and the run parameters are displayed in real time over the course of the run.
8