Ubee Interactive
Deploying and Troubleshooting the Wireless Network
Ubee DVW326 Advanced Wireless Voice Gateway Subscriber User Guide • March 2014
85
5. Use the attenuation value from the materials table above in the following formula:
Formula:
(Transmit Power,
use -30dBm
)
–
(Receiver Sensitivity,
use RSSI value
)
=
Allowable Free Space Loss
Allowable Free Space Loss
÷
Materials Attenuation Value
=
Optimal Distance in Feet Between the Cable Modem and a Wireless Client
Example:
(-30dBm)
-
(-67dBm)
=
37dBm (allowable free space loss for a 54Mbps
connection)
37dBm
÷
.24db/foot (for open space)
=
154.16 feet
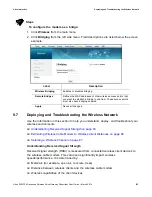
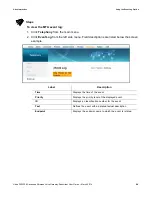
6. Once you know the optimal feet distance between individual wireless clients and the
wireless cable modem, you may resolve and prevent some performance issues.
7. Check the wireless signal strength and speed of the computer connected wirelessly to
the DVW326. Instructions for checking speeds are provided for both a Windows and a
Mac computer in the table below. If the wireless computer is not connected, refer to
Connecting a Wireless Device on page 13
.
Human Body
3dB
Trees (Note 2)
0.15dB / foot
Note 1
: Different types of concrete materials are used in different parts of the world and the thickness
and coating differ depending on whether it is used in floors, interior walls, or exterior walls.
Note 2
: The attenuation caused by trees varies significantly depending upon the shape and thickness
of the foliage.
Attenuation Considerations at 2.4GHz
Material
Attenuation