106636-04 - 8/22
49
X-2
Installation, Operating & Service Manual
Appendix B
Water Quality and Boiler Additives
The heat exchanger used in this boiler is made from
cast-iron. Once filled with water, it will be subjected
to effects of corrosion as well as fouling from any
debris introduced from the system. Take the following
precautions to minimize chance of severe heat
exchanger damage caused by corrosion and/or
overheating.
1.
Flush system before connecting boiler.
In a replacement installation, flushing system will
remove impurities, such as sediment, solder flux,
metal shavings and traces of old boiler additives.
Even if system is new, do not omit this step – new
systems will contain flux and may even contain
other impurities listed above.
Flush system completely and repeat if necessary
to completely remove these contaminants. If
necessary, a cleaning agent may be used to
assist in system cleaning. See Section 15 Start-up
and Checkout for recommended cleaners.
2.
Make sure the system is tight-
this is the single most important guideline.
Tap water contains dissolved oxygen which
causes corrosion. In a tight system, this oxygen
comes out of solution and is quickly removed from
system through automatic air vent. System then
remains essentially free of oxygen.
If system is not tight, however, frequent additions
of make-up water can expose heat exchanger
to oxygen on a continuous basis. In addition,
frequent additions of hard make-up water
can cause calcium deposits to collect in heat
exchanger, causing severe damage. To minimize
additions of make-up water.
A. Inspect system thoroughly for leaks before
putting it into service.
B. If system includes underground piping
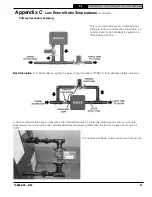
or other piping in which a leak might go
undetected, consider isolating boiler from the
system with a heat exchanger.
C. Make sure expansion tank is properly sized
and in good condition, if it is not, safety relief
valve may open frequently, resulting in regular
additions of make-up water.
D. If an automatic fill valve is installed,
installation of a water meter in fill line is
strongly recommended so routine additions
of make-up water can be detected and their
cause corrected.
3.
Non-metallic tubing
- even if system is tight,
oxygen can be introduced into system through
some types of non-metallic tubing used in radiant
or snow melt systems.
Other non-metallic tubing is equipped with an
oxygen barrier to prevent migration of oxygen
into water. If boiler is to be installed in a system
containing non-metallic tubing without an oxygen
barrier, it must be isolated from boiler with a heat
exchanger.
4. Water chemistry, antifreeze, and boiler water
additives – improper boiler water chemistry can
cause the heat exchanger damage described
above, as well as deterioration.
5. Avoid use of petroleum based boiler additives
and ester-based oils/lubricants. These can attack
seals in both boiler and system.
Freeze Protection
If this freeze protection is required, use the following
or its equivalent:
A. Fernox Alphi-11
B. Sentinel X500 Inhibited Polypropylene Glycol
1. Refer to antifreeze manufacturer’s instructions
for required dosage. In general these products
are a blend of glycol (for freeze protection) and
inhibitors (to protect glycol from attacking metallic
system components.
2. Do not add any more antifreeze than is necessary
to protect system from freeze damage.
3. Maximum antifreeze concentration 50%.
4. Test antifreeze and inhibitor concentration
annually.
A. Inhibitor concentration test kit for Fernox
Protector F1, 25 tests per kit. P/N 101148-01.
B. Inhibitor, Fernox Protector F1, 1 pint (500 mL)
P/N 101147-01.
5. Allowance must be made for additional expansion
of glycol solution.
6. Fernox products are available from:
Alent PLC Consumer Products Division
4100 6th Avenue
Altoona, PA 16602
Tel: (972) 547-6002
Email: [email protected]
7. Sentinel products are available from:
Douglas Products and Packaging
1550 E. Old 210 Highway
Liberty, MO 64068
Tel: (877) 567-2560 (Toll Free) and/or selected
HVAC distributors