SARA-G3 series - System Integration Manual
UBX-13000995 - R06
Objective Specification
Design-in
Page 114 of 218
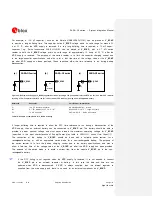
GND clearance on buried layer
below ANT pad
GND
M in.
250 µm
M in. 400 µm
GND clearance on top layer
around ANT pad
Figure 37: GND keep-out area on the top layer around ANT pad and on the very close buried layer below ANT pad
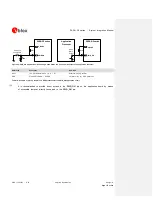
Guidelines for RF transmission line design
The transmission line from the
ANT
pad up to antenna connector or up to the internal antenna pad must
be designed so that the characteristic impedance is as close as possible to 50
.
The transmission line can be designed as a micro strip (consists of a conducting strip separated from a
ground plane by a dielectric material) or a strip line (consists of a flat strip of metal which is
sandwiched between two parallel ground planes within a dielectric material). The micro strip, implemented
as a coplanar waveguide, is the most common configuration for printed circuit board.
provide two examples of proper 50
coplanar waveguide
designs. The first transmission line can be implemented in case of 4-layer PCB stack-up herein
described, the second transmission line can be implemented in case of 2-layer PCB stack-up herein
described.
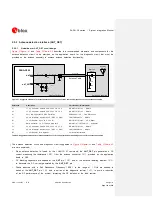
35 um
35 um
35 um
35 um
270 um
270 um
760 um
L1 Copper
L3 Copper
L2 Copper
L4 Copper
FR-4 dielectric
FR-4 dielectric
FR-4 dielectric
380 um
500 um
500 um
Figure 38: Example of 50
coplanar waveguide transmission line design for the described 4-layer board layup