A
B
C
3.4A
A
8
3. Installation
(continued)
3.5A
Determine IP Information:
Before
assigning a static IP address, you'll need to
know the IP address, gateway address and
subnet mask. If you do not have this
information, contact your network
administrator for assistance.
3.5B
Configure Terminal Emulation
Program:
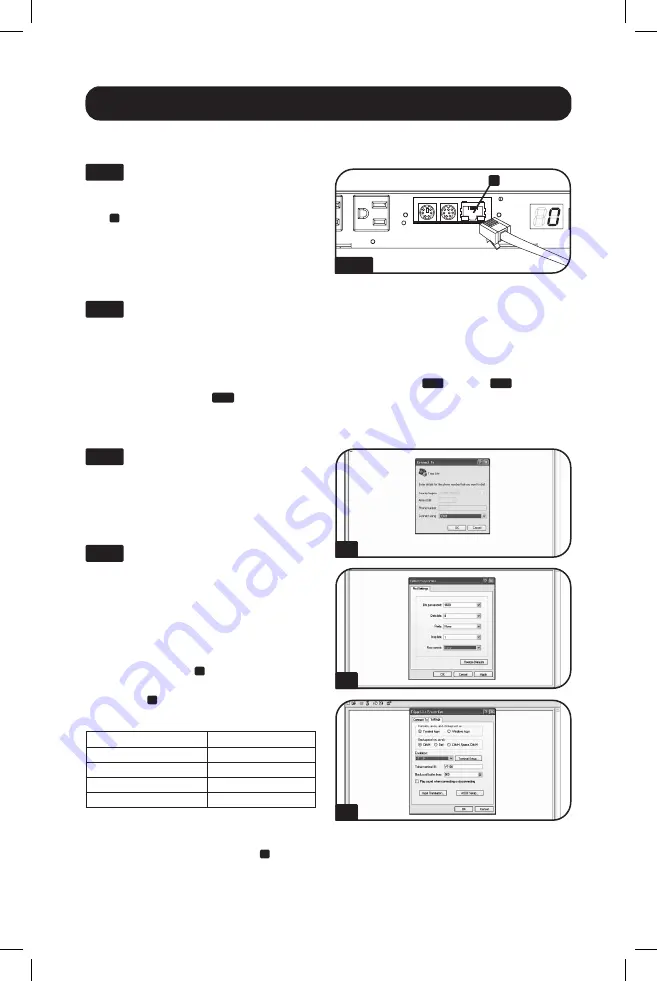
Open a VT100-compatible
terminal emulation program (such as the
HyperTerminal program bundled with
Microsoft
®
Windows
®
) on a computer with
an available DB9 serial port. (A notebook
computer may be the most convenient
choice.) Set the terminal emulation program
to use the COM port
A
that corresponds to
the computer’s DB9 serial port. Specify the
parameters
B
required to communicate with
the PDU terminal interface:
Bits per second:
9600
Data bits:
8
Parity:
None
Stop bits:
1
Flow control:
None
If the terminal emulation program supports
multiple emulation modes, you may also
need to specify VT100 emulation
C
.
3.4 Dynamic IP Address Assignment
3.4B
Discover IP Address:
Contact your network administrator to determine which
dynamic IP address has been assigned to the PDU by the DHCP server. The PDU can be
identified on the DHCP server by referring to its MAC address. (The MAC address is a 12-digit
string in this format: 000667xxxxxx. Refer to the MAC address label attached to the PDU.)
You may wish to request a long-term lease period for the IP address, depending on your
application. After you have discovered the IP address, skip Steps
3.5A
through
3.5F
and
proceed directly to Step
3.6A
.
3.5 Static IP Address Assignment
3.4A
Connect PDU to Network:
While
the PDU is powered, connect a standard
Ethernet patch cable to the RJ-45 Ethernet
port
A
on the PDU.
Note:
This port is not
compatible with PoE (Power over Ethernet)
applications.
The PDU will attempt to obtain
an IP address via DHCP. This may take as
long as several minutes, depending on your
network environment.
21-02-124 933E0A.indb 8
21-02-124 933E0A.indb 8
3/25/2021 2:19:08 PM
3/25/2021 2:19:08 PM