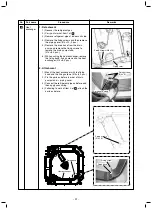
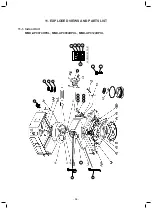
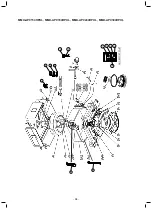
Toshiba
WARNINGS ON REFRIGERANT LEAKAGE
Check of Concentration Limit
The room in which the air conditioner is to be installed
requires a design that in the event of refrigerant gas
leaking out, its concentration will not exceed a set limit.
The refrigerant R410A which is used in the air conditioner is
safe, without the toxicity or combustibility of ammonia, and is
not restricted by laws to be imposed which protect the ozone
layer. However, since it contains more than air, it poses the
risk of suffocation if its concentration should rise excessively.
Suffocation from leakage of R410A is almost non-existent.
With the recent increase in the number of high concentration
buildings, however, the installation of multi air conditioner
systems is on the increase because of the need for effective
use of floor space, individual control, energy conservation by
curtailing heat and carrying power etc.
Most importantly, the multi air conditioner system is able to
replenish a large amount of refrigerant compared with
conventional individual air conditioners. If a single unit of the
multi conditioner system is to be installed in a small room,
select a suitable model and installation procedure so that if the
refrigerant accidentally leaks out, its concentration does not
reach the limit (and in the event of an emergency, measures
can be made before injury can occur).
In a room where the concentration may exceed the limit,
create an opening with adjacent rooms, or install mechanical
ventilation combined with a gas leak detection device.
The concentration is as given below.
The concentration limit of R410A which is used in multi air
conditioners is 0.3kg/m
3
.
NOTE 1 :
If there are 2 or more refrigerating systems in a single
refrigerating device, the amounts of refrigerant should be as
charged in each independent device.
For the amount of charge in this example:
The possible amount of leaked refrigerant gas in rooms A,
B and C is 10kg.
The possible amount of leaked refrigerant gas in rooms D,
E and F is 15kg.
NOTE 2 :
The standards for minimum room volume are as follows.
(1) No partition (shaded portion)
(2) When there is an effective opening with the adjacent room
for ventilation of leaking refrigerant gas (opening without a
door, or an opening 0.15% or larger than the respective
floor spaces at the top or bottom of the door).
(3) If an indoor unit is installed in each partitioned room and
the refrigerant piping is interconnected, the smallest room
of course becomes the object. But when a mechanical
ventilation is installed interlocked with a gas leakage
detector in the smallest room where the density limit is
exceeded, the volume of the next smallest room becomes
the object.
NOTE 3 :
The minimum indoor floor area compared with the amount of
refrigerant is roughly as follows:
(When the ceiling is 2.7m high)
Total amount of refrigerant (kg)
Min. volume of the indoor unit installed room (m
3
)
≤
Concentration limit (kg/m
3
)
e.g., charged
amount (10kg)
Outdoor unit
e.g.,
charged amount (15kg)
Indoor unit
Room A
Room B Room C Room D Room E
Room F
Important
Outdoor unit
Refrigerant piping
Indoor unit
Refrigerant piping
Outdoor unit
Indoor unit
Mechanical ventilation device - Gas leak detector
Very
small
room
Small
room
Medium
room
Large room
0
5
10
10
20
30
15
20
25
30
35
40
m
2
Min.
i
ndoo
r f
loo
r a
rea
Total amount of refrigerant
kg
Range above the
density limit of
0.3 kg/m
3
(countermeasures
needed)
Range below the
density limit of
0.3 kg/m
3
(countermeasures
not needed)
+00A10-005_01EN.book Page 368 Thursday, November 11, 2010 1:15 PM
- 104 -