Owner's Manual for TA150KGMR1 Pneumatic Winches for Personnel Lifting
page 34
A12876A-1214
Frequent Wire Rope Inspection:
•
Use ASME B30.7 as a guideline
for rope inspection, replacement
and maintenance.
•
Check the wire rope, end
connections and end fittings for
corrosion, kinking, bending,
crushing, birdcaging or other signs
of damage.
•
Check the number, distribution and
type of visible broken wires. See
paragraph 3.3.4 d and Figure 23.
•
Check the wire rope for reduction
of rope diameter from loss of
core support, or wear of outside
wires. See Figure 24.
•
Take extra care when inspecting
sections of rapid deterioration
such as sections in contact with
saddles, sheaves, repetitive pickup
points, crossover points and end
connections.
• REMOVE cover and check the O-ring to ensure it is not in need of
replacement, and that all screws are tight. Tighten any screws that may have
loosened during operation.
• CHECK tubing connections for leaks and verify that there are no sharp
bends or kinks in the tube routing.
• REPLACE COVER and check limits for accuracy. Make adjustments to
positions as necessary. See Section 1.7 - Setting Travel Limits.
d
INSPECT THE WIRE ROPE according to the wire rope manufacturer's
recommendations, or follow accepted industry standards for wire rope
inspection.
• Always wear protective clothing when handling wire rope.
• Check the entire length of wire rope for bent wires, crushed areas, broken
or cut wires, corrosion, and other damage. Carefully inspect areas that
pass over sheaves or through roller guides.
• Make sure the load hook or other device is securely attached to the wire
rope, and the wire rope where it is attached is not frayed, corroded,
broken, or otherwise damaged.
• Measure the throat opening, thickness, and twist of the hook. Replace the
hook if it shows signs of damage. See Figure 25.
• Make sure hook latch opens without binding and closes when released.
• Check the anchor holes in the drum and the surrounding area for signs of
wear or distortion.
FOR STANDARD RUNNING WIRE ROPE:
• Wire rope assembly must be replaced if more than 6 wires are broken in
one lay, or if more than 3 wires are broken in one strand in one lay. See
Figure 23
FOR ROTATION RESISTANT WIRE ROPE:
• Wire rope assembly must be replaced if there are 2 or more wire breaks in
6 rope diameters or 4 or more wire breaks in 30 rope diameters. (Note: 6
rope diameters in 1 inch rope is a length of 6 inches.)
e
MOVE THE DRUM with your hands. Check for excessive movement
indicating worn or loose gears or bearings. Excessive movement is caused
by overloading or overheating, and is a sign that your application may
require a larger power winch. Disassemble the winch if necessary. Inspect
bearings, seals, and shafts for wear, distortion, and other damage.
f
PLACE enough weight to keep the wire rope straight and tightly drawn.
• Measure the diameter of the wire rope, especially in areas where wear
is noticeable. Replace the wire rope if the diameter measures below the
minimum diameter at any point. See Figure 24.
g
INSPECT THE FOUNDATION AND RIGGING.
• Check mounting fasteners for stripped threads, wear, and other damage.
• Check the foundation for cracks, corrosion, and other damage.
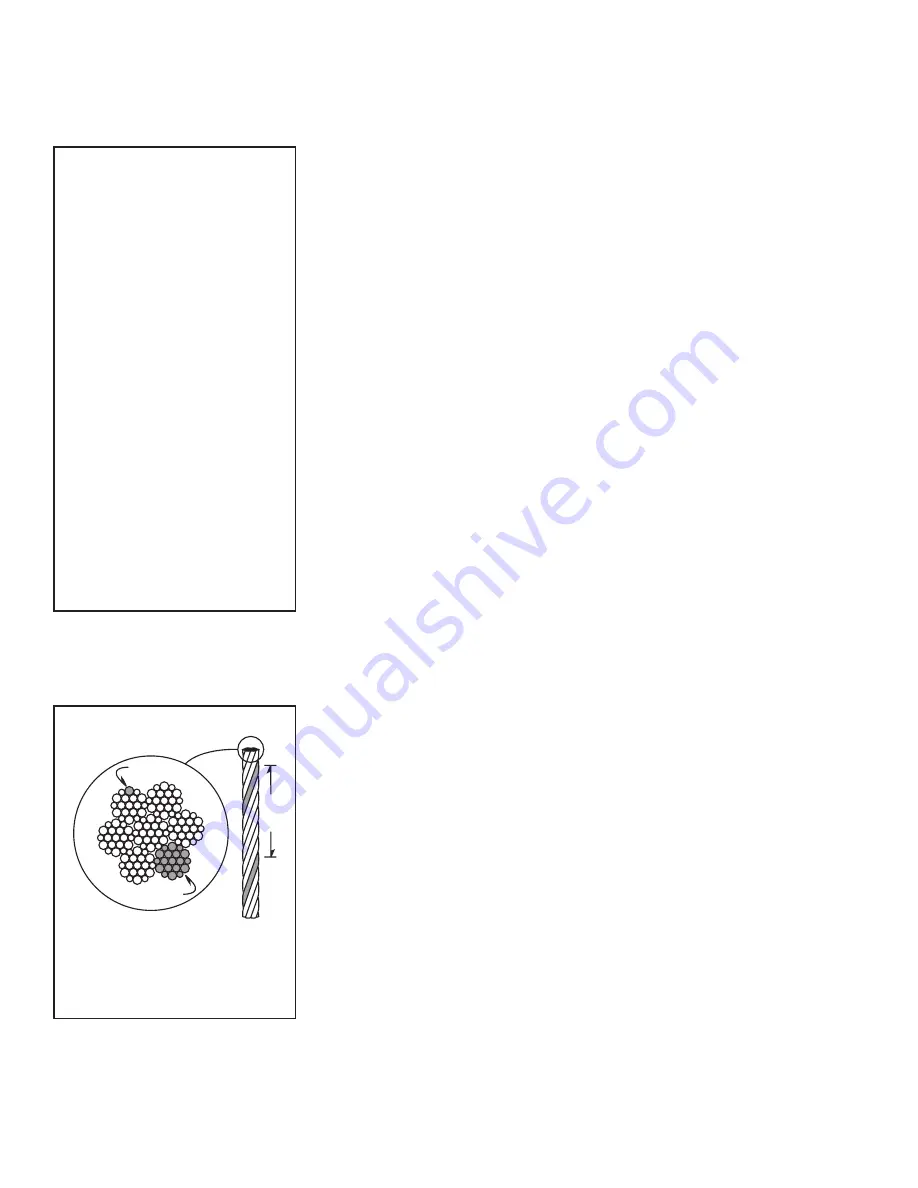
wire
strand
one
lay
Figure 23 – Broken Wires
Wire rope assembly must be re-
placed if more than 6 wires are
broken in one lay, or if more than
3 wires are broken in one strand
in one lay.

































