VCC(drop)
VCC
3 V
t pw
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
0.001
1
1000
Typical Conditions
1 ns
1 ns
t
pw
− Pulse Width − µs
V
CC(drop)
−
V
t
pw
− Pulse Width − µs
V
CC
= 3 V
0
1
t d(BOR)
VCC
V(B_IT−)
Vhys(B_IT−)
V
CC(start)
MSP430G2231-Q1
www.ti.com
SLAS787B – NOVEMBER 2011 – REVISED MARCH 2014
9.12 POR, BOR
(1) (2)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
V
CC
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
V
CC(start)
See
Figure 11
dV
CC
/dt
≤
3 V/s
0.7 × V
(B_IT–)
V
V
(B_IT–)
See
Figure 11
through
Figure 13
dV
CC
/dt
≤
3 V/s
1.35
V
V
hys(B_IT–)
See
Figure 11
dV
CC
/dt
≤
3 V/s
130
mV
t
d(BOR)
See
Figure 11
2000
µs
Pulse duration needed at RST/NMI pin to
t
(reset)
2.2 V, 3 V
2
µs
accepted reset internally
(1)
The current consumption of the brownout module is already included in the I
CC
current consumption data. The voltage level V
(B_IT–)
+
V
hys(B_IT–)
is
≤
1.8 V.
(2)
During power up, the CPU begins code execution following a period of t
d(BOR)
after V
CC
= V
(B_IT–)
+ V
hys(B_IT–)
. The default DCO settings
must not be changed until V
CC
≥
V
CC(min)
, where V
CC(min)
is the minimum supply voltage for the desired operating frequency.
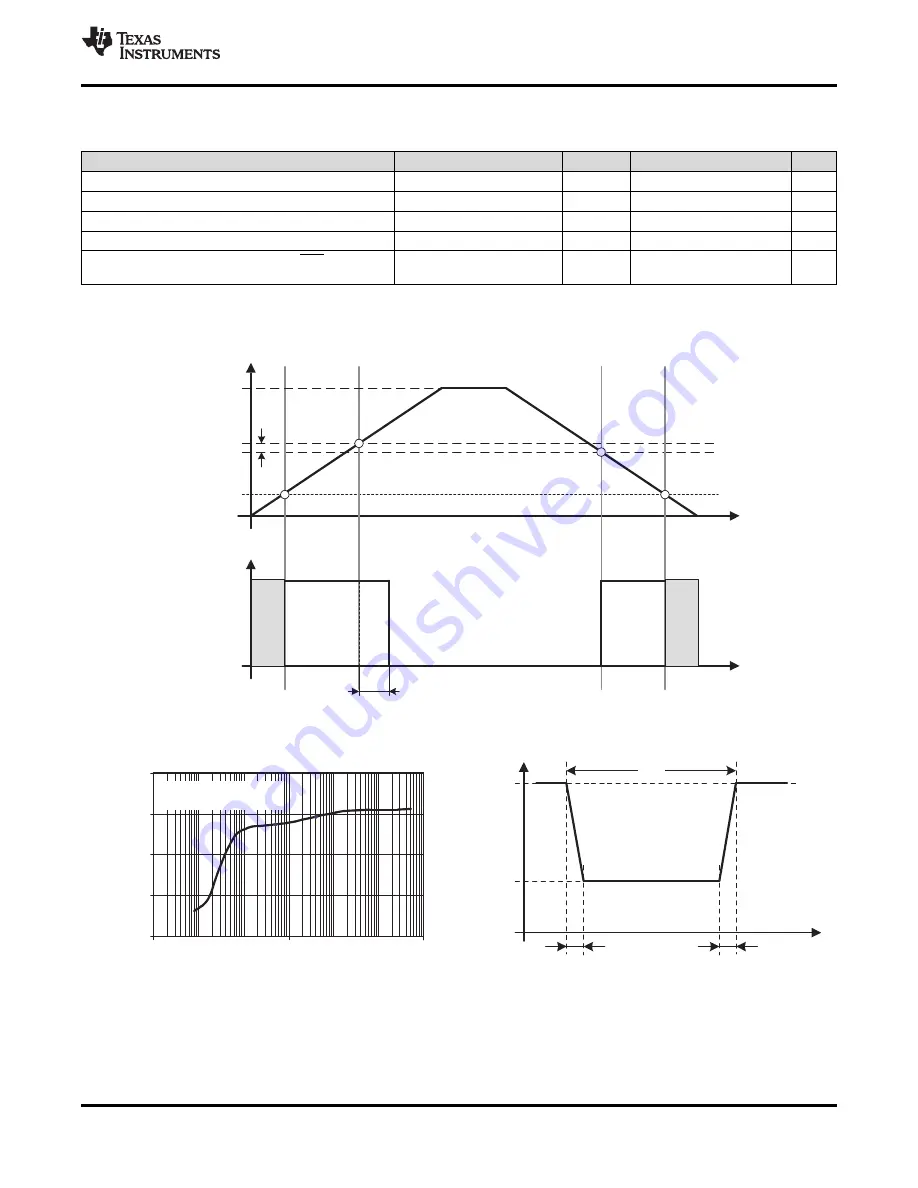
Figure 11. POR and BOR vs Supply Voltage
Figure 12. V
CC(drop)
Level With a Square Voltage Drop to Generate a POR or BOR Signal
Copyright © 2011–2014, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
21
Product Folder Links:
MSP430G2231-Q1
















































