EVM Configuration
18
SNAU236A – June 2018 – Revised December 2018
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
LMK05318EVM User's Guide
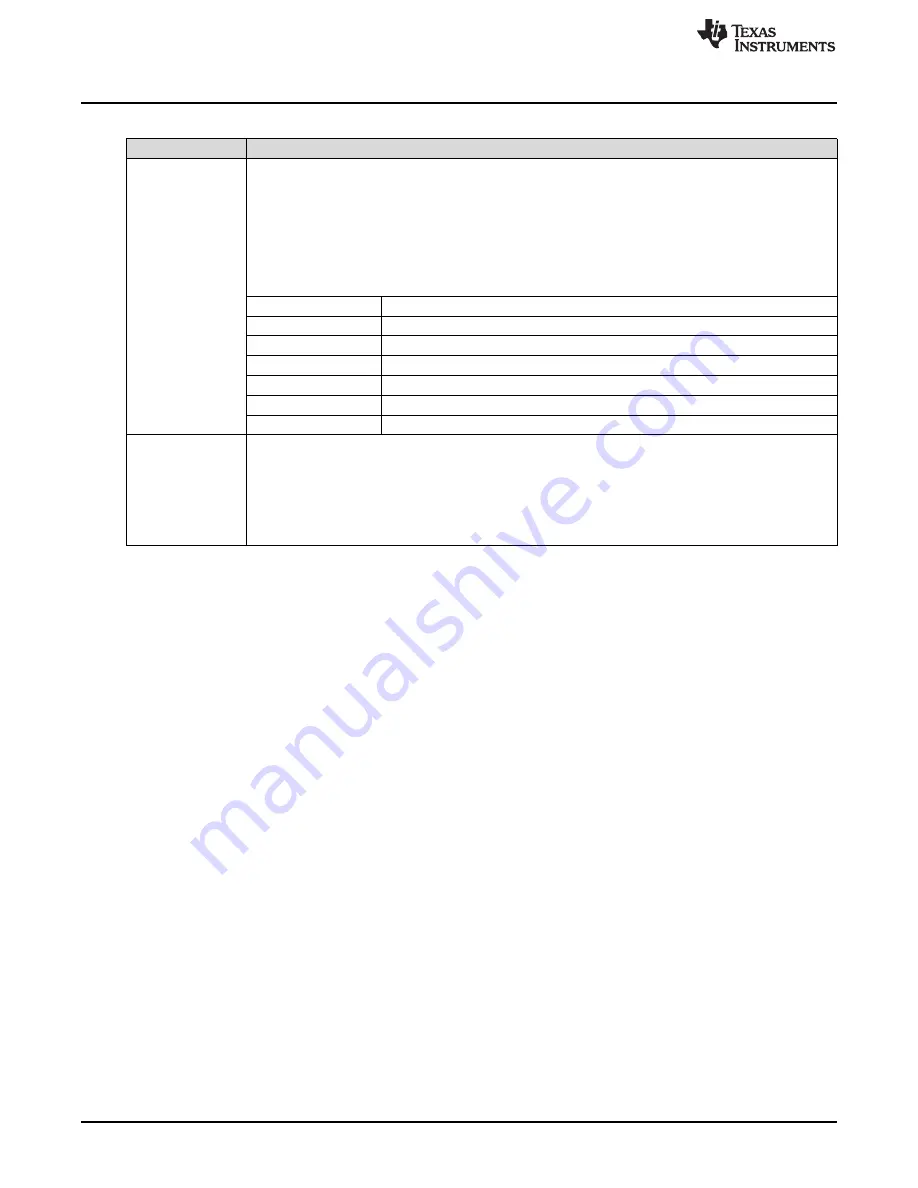
(1)
Logic pins not listed in
are the same as described in
(2)
In ROM + I
2
C Mode, the two I
2
C address LSBs are forced to 00b (address = 0x64h).
Table 11. Logic Pin Descriptions - ROM + I
2
C Mode (HW_SW_CTRL = 1)
(1) (2)
PIN NAME (TYPE)
DESCRIPTION
GPIO[2:0]
(2-level inputs)
GPIO[2:0] Function at POR: ROM Page Selection
GPIO[2:0] pins are sampled on POR to select the ROM page settings used to initialize the registers.
The GPIO[2:0] pins are controlled by S7, S6, and S5, respectively. To configure GPIO[2:0] pins through the
pullup or pulldown resistors only (disable MCU control), set S5[2], S6[2], and S7[2] to OFF. Then, GPIOx
can be pulled up by setting Sy[1] = ON and Sy[3] = OFF, or else pulled down by setting Sy[1] = OFF and
Sy[3] = ON.
GPIO2 Function after POR: DPLL DCO Mode Frequency Increment (FINC)
After POR, the GPIO2 pin can be operated as an FINC input in the same way described for I
2
C
mode (see the GPIO2/FINC description in
).
GPIO[2:0] STATES
ROM PAGE SELECT
000b (Default)
ROM Page 0
001b
ROM Page 1
010b
ROM Page 2
...
...
110b
ROM Page 6
111b
ROM Page 7
STATUS0,
STATUS1/FDEC
(Logic outputs)
Status Outputs
STATUS[1:0] pins are individually programmable status outputs that support NMOS open-drain (requires
external pullup resistor) or 3.3-V LVCMOS driver type. The state of these pins is shown by D7 and D8 when
S2[4] and S3[4] are ON, respectively.
DPLL DCO Mode Frequency Decrement (FDEC)
After POR, the STATUS1 pin can be operated as an FDEC input in the same way described for
I
2
C mode (see the STATUS1/FDEC description in
3.3
XO Input
The LMK05318 has an XO input (XO_P/N pins) to accept a reference clock for the Fractional-N APLLs.
The XO input determines the output frequency accuracy and stability in free-run or holdover modes. For
synchronization applications like SyncE or IEEE 1588, the XO input would typically be driven by a low-
frequency TCXO, OCXO, or external traceable clock that conforms to the frequency accuracy and
holdover stability requirements of the application. For DPLL mode, the XO frequency must have a
non-
integer
frequency relationship with the VCO1 frequency so APLL1 operates in Fractional mode. For APLL
only mode (DPLL not used), the XO frequency can have an integer relationship with the VCO1 and/or
VCO2 frequencies to avoid fractional spurs.
The XO input of the LMK05318 has programmable on-chip input termination and AC-coupled input biasing
options to support any clock interface type.
For flexibility, the EVM provides the three XO input options (use one at a time).
3.3.1
48.0048-MHz Oscillator (Default)
By default, the EVM is populated with a 48.0048-MHz, 3.3-V LVCMOS, low-jitter oscillator (Y1) to drive the
XO_P input of the DUT with the onboard termination and AC coupling. See
. Y1 can be used to
evaluate various frequency configurations. Y1 has multiple overlapped 4-pin SMD footprints (2.5×2.0,
3.2×2.5, 5×7, or 9×14-mm sizes) that allows the user to rework a different XO frequency/model after the
pre-installed component is carefully removed.
3.3.2
External Clock Input
Another option is to feed an external clock to the SMA ports (J5/J4) to drive the XO_P/N inputs
(differential) or XO_P input (single-ended). See
. This path can be connected to the XO_P/N input
pins by placing 0.1-µF capacitors on C81 and C82 and opening C80, C137, and C138. Y1 and U10 should
be powered down when using the external XO input path.















































