Hardware Installation
SY-7ISA
46
2-3.7 Debug LEDs
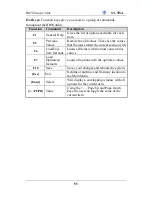
The Debug LEDs give an indication of the status of the system during
boot-up. If the system does not boot-up properly, use the table below to
find out at what point in boot-up sequence the problem arises. A x means
the LED is off, a L means the LED is lit.
Code
Explanation
X
X
X
L
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
Initialization of the chipset. The MCH and ICH registers will be
set to the most conservative values by the BIOS to make sure the
system boots up properly.
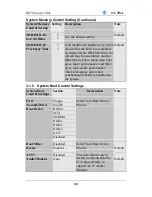
X
X
L
X
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
The BIOS is now decompressing the BIOS code into shadow RAM. Most
of the BIOS code is stored in the BIOS Flash ROM IC in compressed
form to save space. At boot-up this code is decompressed and stored to
RAM for faster execution.
X
X
L
L
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
The checksum for the decompressed code is calculated and checked. The
checksum is calculated by adding all data bytes together and storing the
result in the BIOS ROM. If the calculated checksum is different from the
checksum stored in the ROM, the code stored in the FLASH ROM is
corrupted.
X
L
X
X
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
The chipset (MCH and ICH) registers are set to the values selected by the
user.
X
L
X
L
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
Now the BIOS will set the CPU Vcore voltage and the FSB bus frequency
to the user selected value. If the system stops at this point, the settings
selected by the user are inappropriate. Please select more conservative
settings.
X
L
L
X
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
The Hardware Monitor Functionality is initialized. The settings the user
selected in the BIOS for the Hardware Monitor are written into the
Hardware Monitor registers.
X
L
L
L
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
If the VGA card does not work or is not inserted at all, the system will
display this code for a short period of time.
L
X
X
X
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
At this point the BIOS is initializing the CPU. The L2 cache latency
values are set, and more important, the CPU micro-code is written into the
CPU.
L
X
X
L
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
Now the system is testing the RAM inserted on the board. The screen will
show the BIOS testing the RAM by a running counter. After finishing the
test, the screen will show the amount of RAM in your system.
L
X
L
X
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
The super I/O registers are set to the default values. This includes the
serial, parallel and IR etc settings.
L
X
L
L
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
At this point the IDE busses (primary and secondary) are scanned for
devices. This includes HD drives and ATAPI CD-ROM drives that are
connected to the IDE bus. After scanning the detected devices are
displayed on screen.
L
L
X
X
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
The serial and parallel port registers are set to the values selected by the
user.
L
L
X
L
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
Now the BIOS will scan the peripheral busses for add-on cards. This
includes the PCI and AGP busses. If any add-on cards are detected, the
resources it requires are assigned by the BIOS in accordance with user
settings.
L
L
L
X
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
The ESCD and DMI (Desktop Management Interface) values are checked.
If there are changes, the BIOS will flash the new values into the BIOS
Flash ROM IC.
L
L
L
L
LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1
At this point the BIOS passes control to the Operating System (OS). All
LEDs will be on and will stay on to indicate a successful boot.