127
20. CHANGING THE SETTINGS
• e (water vapor pressure) can be calculated using the following formula.
• The instrument measures the distance with a beam of light, but the velocity of this light varies
according to the index of refraction of light in the atmosphere. This index of refraction varies
according to the temperature and pressure. Near normal temperature and pressure
conditions:
With constant pressure, a temperature change of 1°C: an index change of 1 ppm.
With constant temperature, a pressure change of 3.6 hPa: an index change of 1 ppm.
To perform high accuracy measurements, it is necessary to find the atmospheric correction
factor from even more accurate temperature and pressure measurements and perform an
atmospheric correction.
It is recommended that extremely precise instruments be used to monitor the air temperature
and pressure.
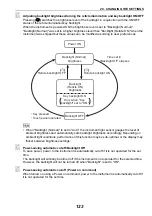
• Enter the average temperature, air pressure and humidity along the measurement beam route
in "Temperature", "Pressure" and "Humidity".
Flat terrain:Use the temperature, pressure and humidity at the midpoint of the line.
Mountainous terrain:Use the temperature, pressure and humidity at the intermediate point (C).
If it is not possible to measure the temperature, pressure and humidity at the midpoint, take such
measurements at the instrument station (A) and the target station (B), then calculate the average
value.
Average air temperature
: (t1 + t2)/2
Average air pressure
: (p1 + p2)/2
Average humidity
: (h1 + h2)/2
• If the weather correction is not required, set the ppm value to 0.
E
6.11 10
7.5 t
×
(
)
t 237.3
+
(
)
----------------------------
×
=
e
h
E
100
----------
×
=
Humidity h
1
Humidity h
2