' SLS loudspeakers Inc., 2002. All rights reserved.
17
Conclusions
Based on the LASS program simulation, measurement data and analysis of various line
array design concepts, the following conclusions can be stated that:
1. Implementation of compression drivers in line array systems, where a coherent
planar wavefront is necessary to achieve line source performance, imposes
significant design difficulties and results in compromising the acoustical
parameters of such a system.
2. The PRD 1000 planar ribbon driver allows for elegant line array design solutions
and provides a means for achieving consistent line source properties and wide
symmetrical horizontal dispersion over a wide frequency range.
3. The RLA1 ribbon line array system, based on the PRD1000 driver, demonstrates
far superior performance over line arrays based on conventional compression
driver design.
The RLA1 provides:
-
much better coverage consistency, SPL deviation along the RLA1 coverage area is
significantly lower, without pronounced SPL peaks and dips and areas with
dramatic loss of high frequency energy, inherent to other line arrays.
- easily predictable coverage zone borderlines
-
lower SPL loss with distance, within the coverage zone
-
effective elimination of lobing and comb-filtering
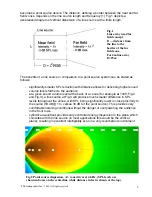
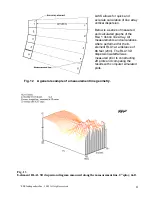
4. The vertical polar diagram, as commonly defined, is not applicable to line arrays,
since it is valid, only if measured in a system’s far field.
A line array’s dispersion diagram, observed along the array’s length (in the
simplest case this would be vertical dispersion) is a specific characteristic for a
specific distance. If measured, it is only valid for the distance at which the test was
performed. A dispersion diagram should be measured along the polygonal
measurement line defined above, not around the circle as for polars.
5. A line array’s vertical dispersion has an infinite three-dimensional characteristic,
which depends on distance. It cannot be fully described by measurement data. It
can only be modeled with the help of such programs as the LASS, using
mathematical means, allowing for a near-field numerical simulation accounting for
the distance from each element and cannot be modeled by other programs that
use measured polar diagrams or far-field modeling only.
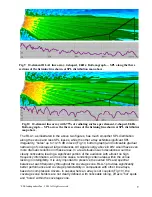
6. The LASS Line Array Simulator Software is a powerful program for easy and quick
prediction of line array dispersion in the vertical plane (or horizontal plane if the
array is positioned accordingly). The results of simulation closely correlate with
actual measurements of the RLA1 line array. The comparison of simulated and
measured data also proves that the RLA1 possesses a coherent planar wavefront,
as assumed in LASS, and demonstrates line source behavior over a wide
frequency range. Line arrays based on compression drivers, can be modeled by
introducing gaps between radiators with a certain filling coefficient.