6. Navigation and Control System
SMF-MP10S User guide V1.1 Shanghai Seer Intelligent Technology Corporation
29
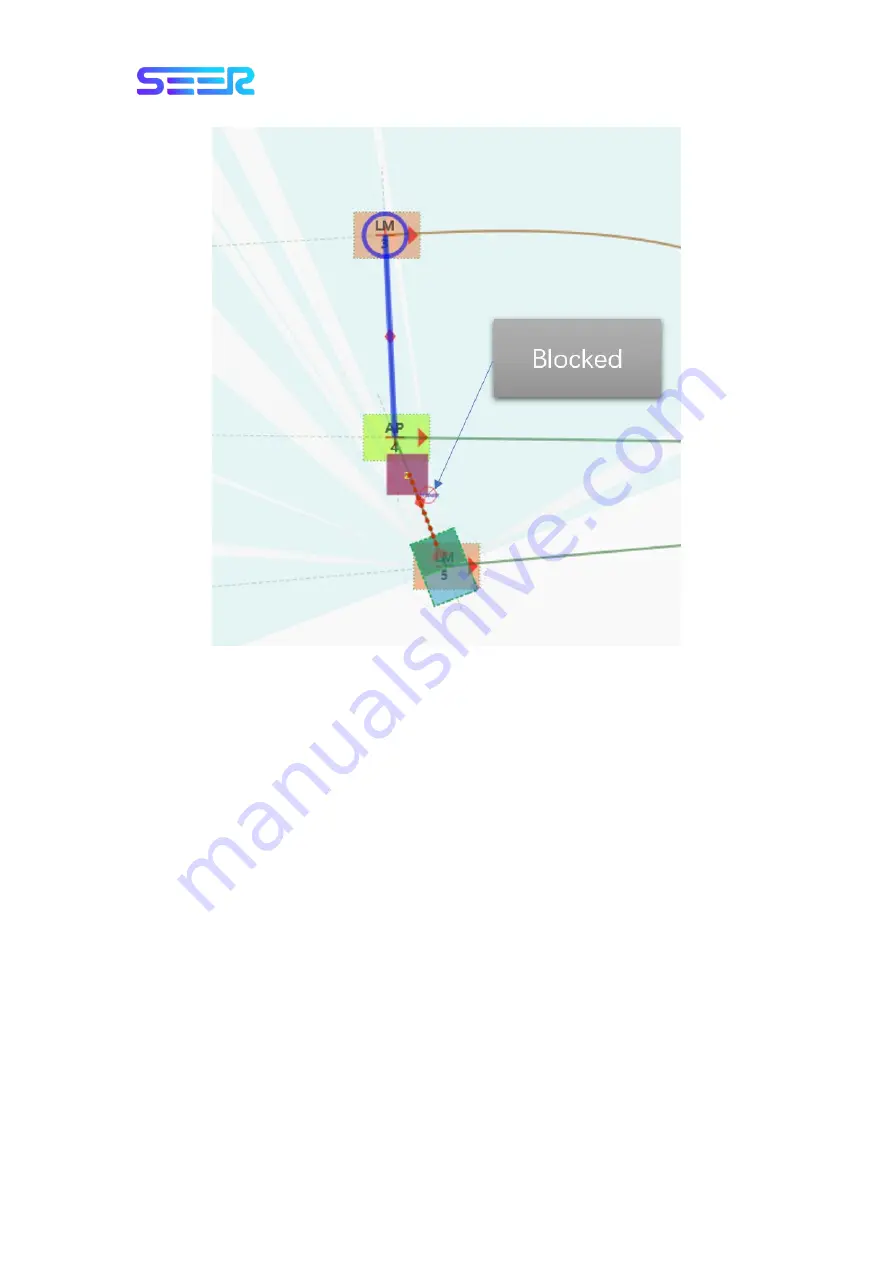
When it detects a virtual obstacle on the path, the robot will navigate the local path to avoid
obstacles and stop.
6.5 Task Planning and Action Planning
When the robot receives a task instruction, it will split the instruction into a sequence of
actions. For example, the task of recognizing and picking up the cargo is issued to the jacking
cart, the instruction issued will be decomposed into three parts during the task planning: 1.
Recognize the location of the cargo; 2. Navigate to the location of the cargo; 3. Perform the
pickup action. Only after each action is successfully actuated, the task instruction is
considered to be complete.
The action planning is to plan the robot’s own equipment to perform each action. For
example, 1. To recognize the location of the cargo, the action planning will call the camera to
recognize the location of the cargo based on the appropriate recognition files. 2. To navigate
to the location of the cargo, the action planning will call the local path navigation to make
the robot move to the destination. 3. To perform the pickup action, the robot will rotate the
pickup motor to load the cargo.
Under the control of RoboShop, each navigation instruction can be accompanied by a task
instruction. In the dispatching mode of the robot, each path can be accompanied by a task
instruction.






























