– 11 –
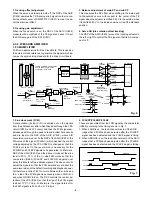
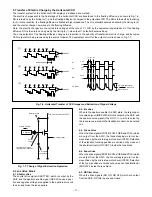
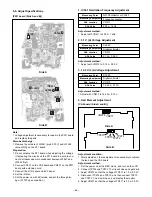
Fig. 1-6. Horizontal Transfer of CCD Imager and Extraction of Signal Voltage
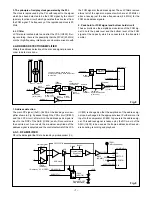
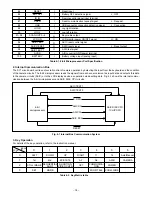
Fig. 1-7. Theory of Signal Extraction Operation
Reset gate pulse
12V Pre-charge drain bias
(
PD
)
Direction of transfer
Voltage output
Electric
charge
H Register
Floating diffusion gate is
floated at a high impedance.
C is charged
equivalently
5. Transfer of Electric Charge by the Horizontal CCD
The transfer system for the horizontal CCD emplays a 2-phase drive method.
The electric charges sent to the final stage of the horizontal CCD are transferred to the floating diffusion, as shown in Fig. 1-6.
RG is turned on by the timing in (1), and the floating diffusion is charged to the potential of PD. The RG is turned off by the timing
in (2). In this condition, the floating diffusion is floated at high impedance. The H1 potential becomes shallow by the timing in (3),
and the electric charge now moves to the floating diffusion.
Here, the electric charges are converted into voltages at the rate of V = Q/C by the equivalent capacitance C of the floating
diffusion. RG is then turned on again by the timing in (1) when the H1 potential becomes deep.
Thus, the potential of the floating diffusion changes in proportion to the quantity of transferred electric charge, and becomes
CCD output after being received by the source follower. The equivalent circuit for the output circuit is shown in Fig. 1-7.
H1
H2
H1
H2
H1 HOG
RG
CCD OUT
PD
Floating diffusion
(1)
H1
H2
H1
H2
H1 HOG
RG
CCD OUT
PD
(2)
H1
H2
H1
H2
H1 HOG
RG
CCD OUT
(3)
H1
H2
RG
CCD OUT
3.5V
0V
3.5V
0V
15.5V
12V
Black level
RG pulse peak signal
Signal voltage
(1) (2) (3)
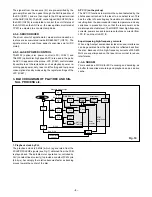
6. Lens drive block
6-1. Shutter drive
The shutter drive signal (SHUTTER) which is output by the
ASIC and the aperture enable signal (AE SW) cause a posi-
tive and negative voltage are applied to the aperture drive coil
to open and close the lens aperture.
6-2. Iris drive
When in the aperture enable (AE SW) state, the target aper-
ture value signal (IRIS PWM) which is output by the ASIC and
the aperture value signal (HALL OUT +/–) which is output by
the lens are compared so that feedback control can be carried
out.
6-3. Focus drive
When the drive signals (FRSTB, FCW, FOEB and FCLK) which
are output from the ASIC, the focus stepping motor is sine-
wave driven by the micro-step motor driver (IC953). Detection
of the standard focusing positions is carried out by means of
the photointerruptor (FOCUS PI) inside the lens block.
6-4. Zoom drive
When the drive signals (ZRSTB, ZCW, ZOEB and ZCLK) which
are output from the ASIC, the zoom stepping motor is sine-
wave driven by the micro-step motor driver (IC954). Detection
of the zoom positions is carried out by means of photoreflector
(ZOOM PI) inside the lens block.
6-5. ND filter drive
When the drive signals (ND ON, ND OFF) which are output
from the ASIC, ND filter opens and closes.
Содержание IDC-1000ZE iDshot
Страница 45: ...OVERALL WIRING 基板間結線図 ...
Страница 46: ...Apr 01 3 780 NS Printed in Japan SANYO Electric Co Ltd Osaka Japan ...