REV-31-1230-QS-01
Copyright © 2018 REV Robotics, LLC
2
SERVO-PWM INPUT
A motor’s speed is controlled by varying the voltage that is applied to it. The SPARKmini’s output voltage can be
controlled by sending it an extended-range servo-PWM pulse. The extended 500µs to 2500µs servo-pulse corresponds to
full-reverse and full-forward rotation with 1500µs as the neutral position (no rotation). The pulses are proportionally
related to the motor output duty cycle, therefore variable speed can be achieved with pulses in between the extremes. The
following table describes the pulse ranges in more detail.
Table 1 - Control Signal Pulse Ranges
Pulse Width (
p
in µs)
Full Reverse
Prop. Reverse
Neutral
Prop. Forward
Full Forward
p
≤
500
500 <
p
< 1490
1490
≤
p
≤
1510
1510 <
p
< 2500
2500
≤
p
ZERO-POWER BEHAVIOR
When the SPARKmini is receiving a neutral command it will not provide any power to the attached motor. There are two
options for how the SPARKmini handles this zero-power state:
Brake
- Motor terminals are shorted to each other to dissipate electrical energy, effectively braking the motor.
Coast
- Motor terminals are disconnected, allowing the motor to spin down at its own rate.
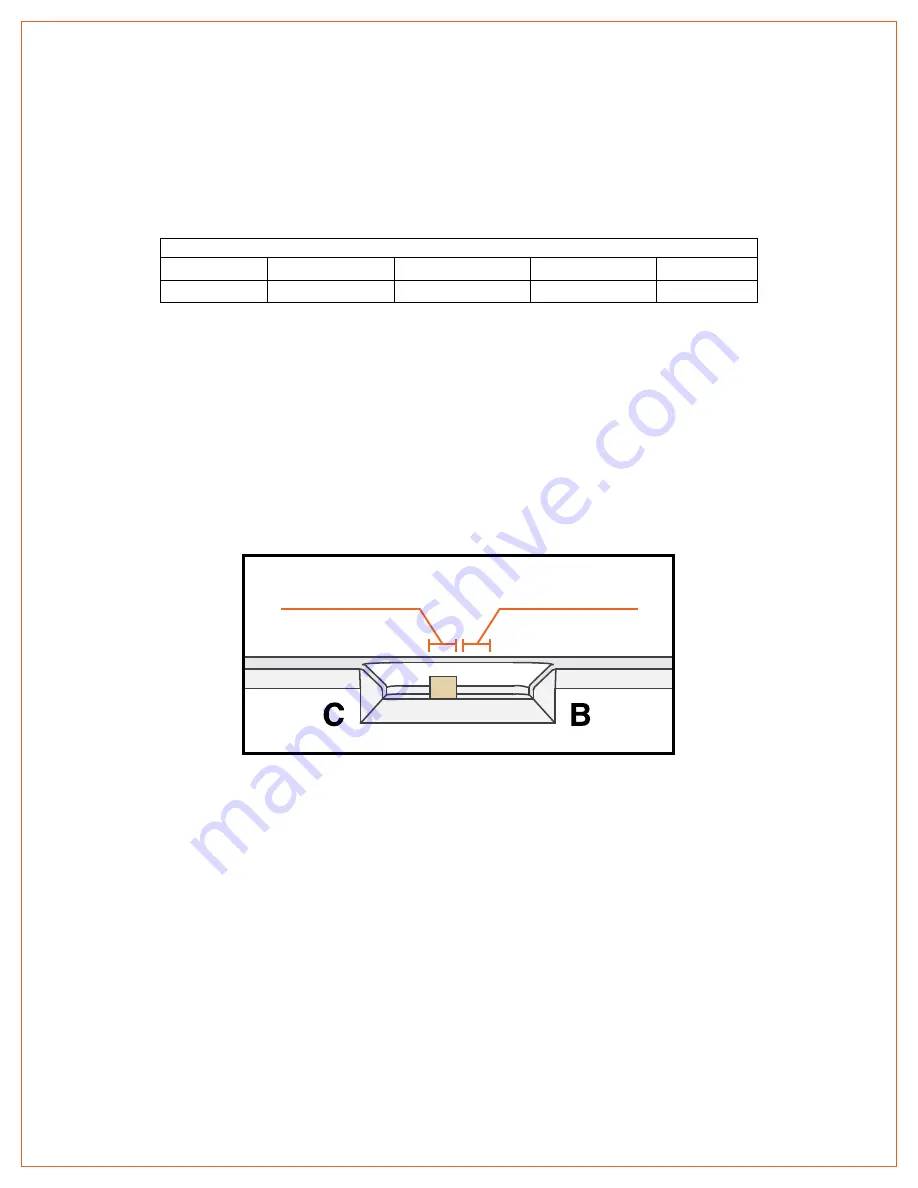
The zero-power behavior can be selected via a switch located towards the center of the SPARKmini housing, shown in
Figure 2. Each mode can be selected by sliding the switch to either the Brake (B) or Coast (C) positions.
Figure 2 - Brake Coast Switch
The SPARKmini will indicate whether it is in Brake or Coast mode via the Status LED, located in the center of the housing,
whenever it is outputting zero-power. Solid or flashing blue indicates Brake Mode while solid or flashing yellow indicates
Coast Mode. See the LED Status Codes section for more details.
Coast
Brake





















