iBreeze CPAP Clinical Guide
18
7.5 Events
Automatically pressure regulation rules
The treatment pressure required for the patient to keep the upper airway clear may vary with
body position and sleep state of the patient throughout the night. To avoid uncomfortable feelings
resulting from high-level mask pressure, the adequate treatment pressure is expected to be the
lowest pressure that is enough to keep patency of the upper airway. The device adjusts the
treatment pressure according to the detection of the following several types of sleep events,
apnea, hypopnea, snoring, flow limitation, RERA and periodic breathing. A fuzzy adaptive
algorithm is applied to detect the events mentioned above. Treatment pressure is adjusted based
on the detecting results, as obstructive apnea, hypopnea, snoring and flow limitation lead to
pressure increasing, but the increasing amplitudes get more and more moderate sequentially. No
therapy adjustments are made in response to the other events. Once in normal breathing again,
the treatment pressure reduces gradually.
By the automatic pressure adjustment method mentioned above, the average treatment pressure
resides in a relative lower level, which offers a better therapy compliance. This function is
enabled in APAP, APAPW Mode.
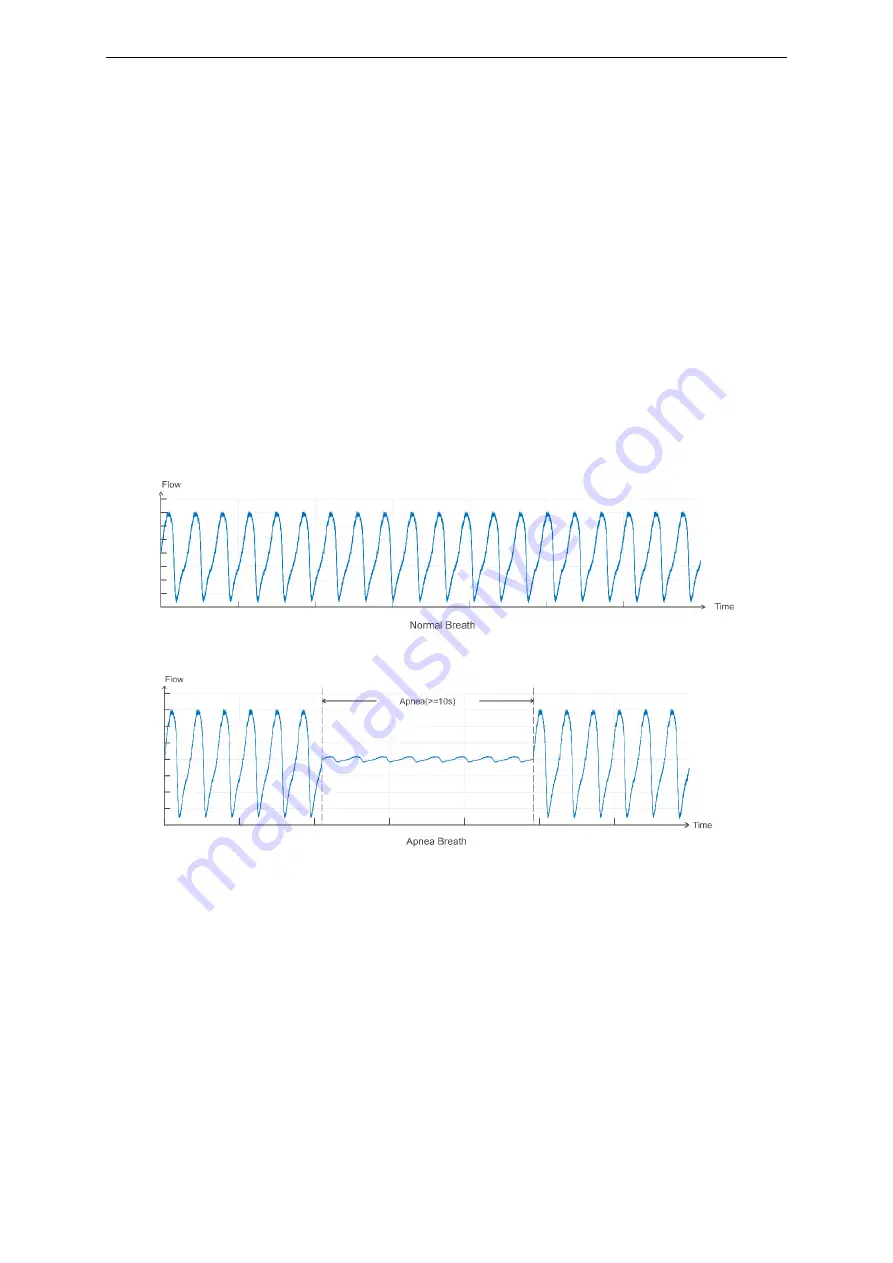
Apnea
Apnea is defined as amplitude of the patient flow reduces to 10% of its corresponding value
when in normal breathing and lasts for over 10 seconds.
Once the device senses a latent apnea, the device delivers a test pulse to identity patency of the
upper airway. If the apnea is confirmed and the airway is clear, then central apnea is reported
and no action is taken. If the airway is obstructed, obstructive apnea is reported and treatment
pressure increases in an adaptive way as soon as breathing efforts detected. The treatment
pressure reduces gradually when in continuous normal breathing.
Hypopnea
Hypopnea is defined as amplitude of the patient flow reduces to 50% of its corresponding value
when in normal breathing and lasts for over 10 seconds.










































