..\Manuals\RCI-200-RFM rev.B.doc
Page 5 of 8
RFM Communication Option:
The -RFM communications option to the RCI series utilizes license-free spread spectrum radio
frequency transmissions to exchange the signal data between a host and its remote(s). There are two
Modes of Operation
available: 1) Standard mode and 2) Repeater mode.
In the
Standard
mode of operation, the host unit communicates directly with all remotes. This is the
fastest method for communication. This mode requires that all remotes are within line-of-sight of the
host.
In the
Repeater
mode of operation, some remote units may not be in direct line-of-sight of the host but
are in line-of-sight of another remote. This second remote must be in line-of-sight of the host so that it
can pass on the signal from the hoist to the initial remote.
The repeater mode is slower than the standard mode and it is suggested that it only be used where
necessary.
All units in a system must be set to the same Mode of Operation.
Even if only one
repeater is required in a system, all units (host & remotes) must be set to the Repeater mode.
In addition there are two types of
Topologies
that can be configured: 1) Point-to-Point and 2) Host-to-
Multipoint.
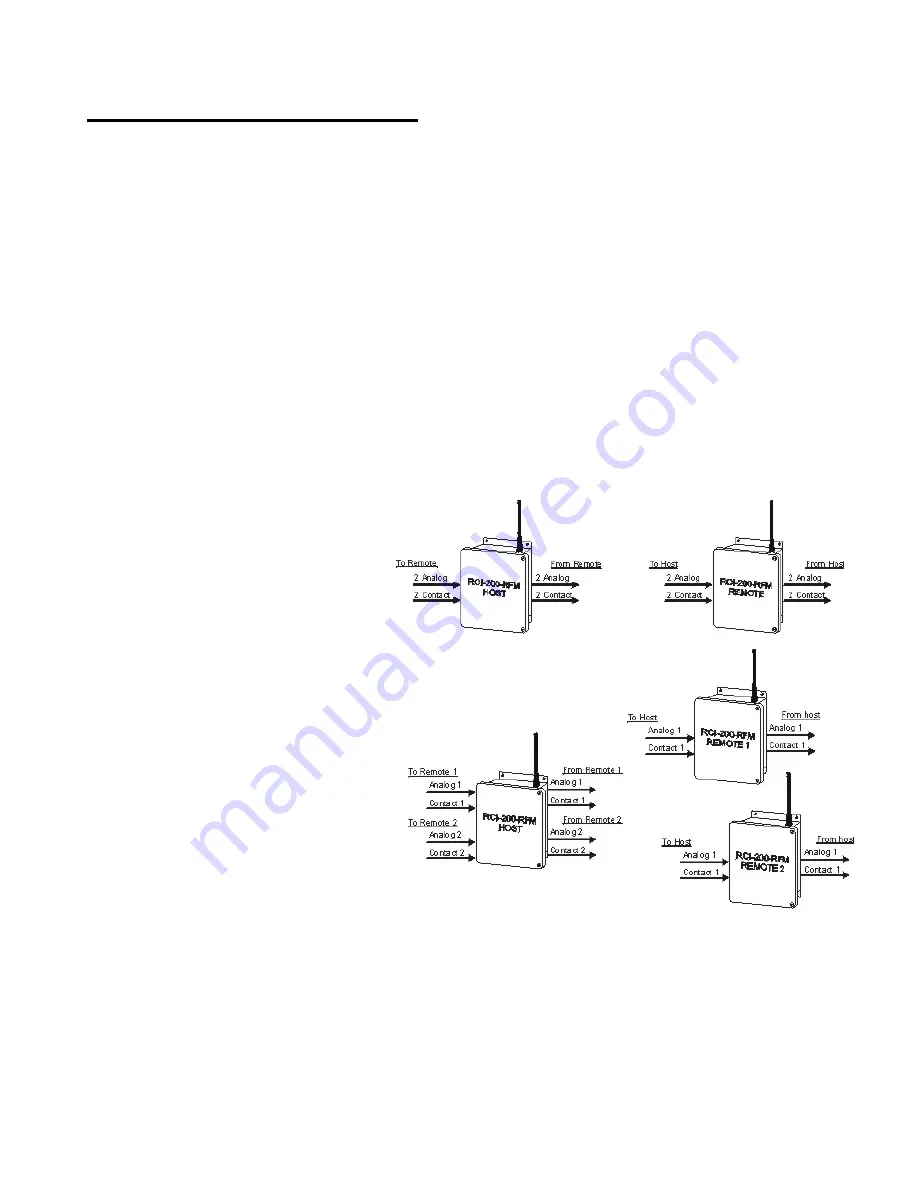
In a
Point-to-Point
topology one host
communicates with one remote. The
two exchange all their signals with one
another. The remote is configured as
remote #1 even though it is the only
remote in the system.
In a
Host-to-Multipoint
topology one
host communicates to several remotes.
Each remote is assigned an address
(1,2,3, etc.) so that the host may
distinguish between them. There may at
most be as many remotes as there are
inputs & outputs on the host.
For example, an RCI-200 system, having
two analog/contact inputs and outputs,
may communicate with up to two remotes
each having one analog/contact input and
output. In this case all
#1 inputs and
outputs on the host correspond to the
#1 inputs and outputs on remote #1
and all
#2 inputs and outputs on the host correspond to the
#1 inputs and outputs on remote #2
. The second analog/contact input and output on each of the two
remotes would be unused.
A
Network ID
allows multiple RFM systems to co-exist within close proximity without interfering with
one another. There are four Network ID’s to choose from: A, B, C or D. The host and its remote(s)
must be set to the same Network ID in order for them to communicate with each other.
































