www.parweld.com
Manganese steels
The effect on manganese steel of slow cooling from
high temperatures is enbrittlement. For this reason it
is absolutely essential to keep manganese steel cool
during welding by quenching after each weld or skip
welding to distribute the heat.
Cast iron
Most types of cast iron, except white iron, are
weldable. White iron, because of its extreme
brittleness, generally cracks when attempts are made
to weld it. Trouble may also be experienced when
welding white-heart malleable, due to the porosity
caused by gas held in this type of iron.
Copper and alloys
The most important factor is the high rate of heat
conductivity of copper, making preheating of heavy
sections necessary to give proper fusion of weld and
base metal.
Types of electrodes
Arc welding electrodes are classified into a number
of groups depending on their applications. There are
a great number of electrodes used for specialized
industrial purposes which are not of particular interest
for everyday general work. These include some low
hydrogen types for high tensile steel, cellulose types
for welding large diameter pipes, etc. The range of
electrodes dealt with in this publication will cover the
vast majority of applications likely to be encountered;
are all easy to use and all will work on even the most
basic of welding machines.
Metals being joined & electrode comments
Mild steel
6013 ideal electrodes for all general purpose work.
Features include outstanding operator appeal, easy
arc starting and low spatter.
10
O
pera
tIO
n
Mild steel
7014 all positional electrode for use on mild and
galvanized steel furniture, plates, fences, gates, pipes
and tanks etc. Especially suitable for vertical down
welding.
Cast iron
99% nickel suitable for joining all cast irons except
white cast iron
Stainless steel
318l-16 high corrosion resistance. Ideal for dairy work,
etc. On stainless steels.
6.3
TIG Welding guide
Controls used
2T/4T sets the trigger to momentary or latching for
longer welding runs.
Voltage adjustment knob, allows the adjustment of
the post gas flow time after welding stops.
Current adjustment knob which controls the output
current.
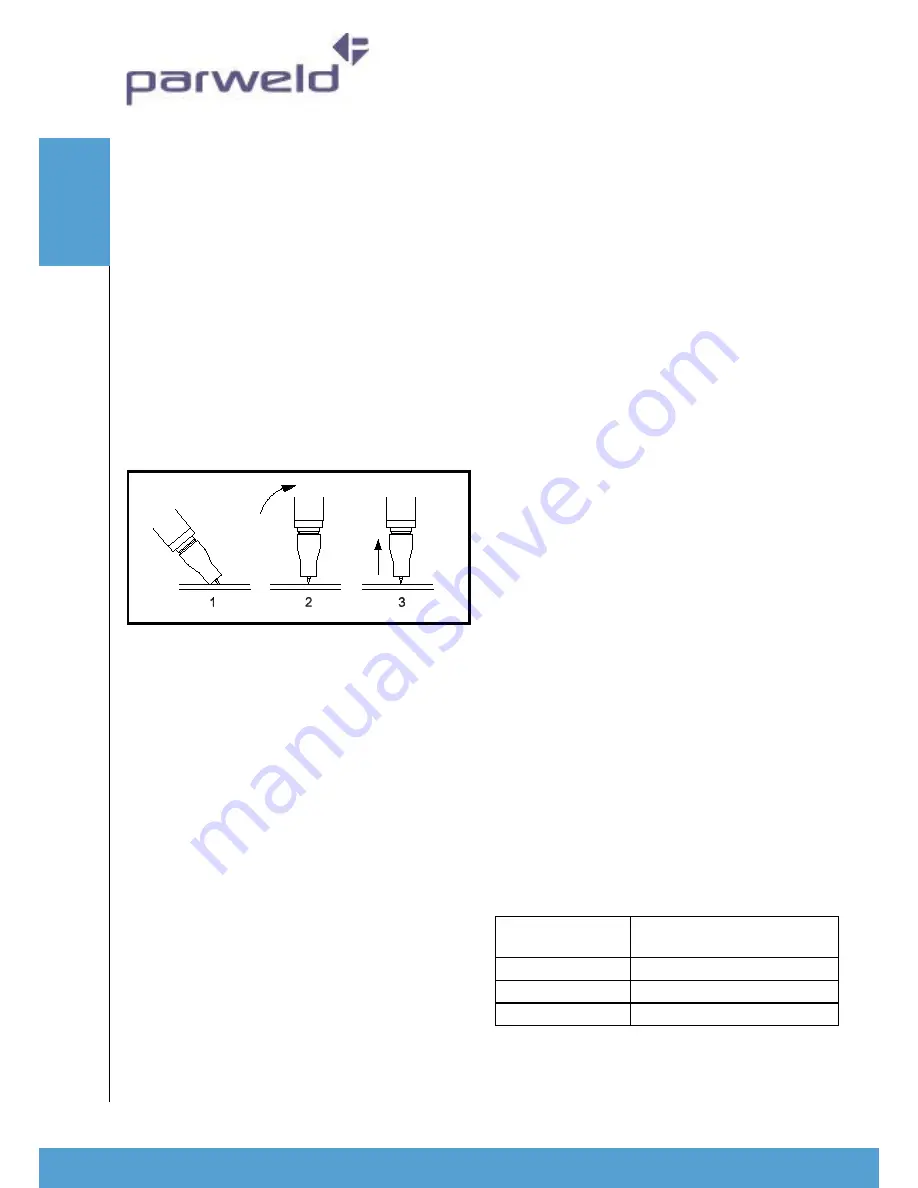
Torch starting in Lift TIG mode
Ensure the gas supply is switched on. Briefly contact
the tip of the tungsten electrode down onto the work
piece with the torch at around 70
0
from vertical,
depress the torch trigger to switch on the welding
power and the gas flow. Lift the torch up from the
work piece to draw out an arc. To prevent melting of
the end of the tungsten the machine will increase the
output current when it detects the rise in arc voltage
as the tungsten is lifted from the work piece. TO stop
welding release the trigger
Note in 4T mode the trigger should be release during
welding and then depressed briefly to stop the
welding process.
TIG welding guide ranges
Electrode
diameter
DC current (amps)
0.040” (1.0mm)
30 – 60
1/16” (1.6mm)
60 – 115
3/32” (2.4mm)
100 – 165
Содержание XTI-601 MP
Страница 1: ...INSTRUCTION MANUAL...
Страница 2: ...Operator Manual ISSUE 1 XTI 601 MP...


































