BASIC TIG WELDING GUIDE
Tig welding cable connection
Connect the TIG torch to the Negative terminal and the work
lead to the Positive terminal for direct current straight polarity.
Direct current straight polarity is the most widely used polarity
for DC TIG welding. It allows limited wear of the electrode
since 70% of the heat is concentrated at the work piece.
Connect the gas hose on the TIG torch to the gas outlet on
the front panel of the machine and the control lead plug to the
socket on the front panel of the machine.
Basic control setups
.
DC welding non pulse
Select DC current (7)
Select non pulse (16)
Select 2T trigger (8)
Select Tig mode (17)
Adjust pre-flow to mid range (3)
Adjust down slope to mid range (6)
Adjust post flow to mid range (15)
Adjust welding current to desired level (4)
AC welding non pulse
Select AC current (7)
Select non pulse (16)
Select 2T trigger (8)
Select Tig mode (17)
Adjust pre-flow to mid range (3)
Adjust down slope to mid range (6)
Adjust post flow to mid range (15)
Adjust welding current to desired level (4)
Adjust cleaning control to mid range (14)
Additional pulse settings
Set frequency to mid range (12)
Set pulse duration to mid range (13)
Set background current to mid range (5)
Select pulse option (16)
TIG welding guide ranges
Electrode diameter
dc current (amps)
0.040” (1.0mm)
30 – 60
1/16” (1.6mm)
60 – 115
3/32” (2.4mm)
100 – 165
Tungsten electrode types
Electrode type Welding application
colour
code
Thoriated 2%
dc welding of mild steel,
stainless steel and copper. Excellent arc
starting, long life, high current carrying
capacity.
Ceriated 2%
dc welding of mild steel, stainless steel,
copper, aluminium, magnesium and
their alloys longer life, more stable arc,
easier starting, wider current range,
narrower more concentrated arc.
Guide for selecting filler wire diameter
Filler wire diameter
dc current range
1/16” (1.6 mm)
20 - 90
3/32” (2.4 mm)
65 - 115
1/8” (3.2 mm)
100 - 165
3/16” (4.8 mm)
200-350
The filler wire diameter specified is a guide only, other
diameter wires may be used according to the welding
application.
Shielding gas selection
Alloy
shielding gas
Aluminium & alloys
argon
Carbon steel
argon
Stainless steel
argon
Nickel alloy
argon
Copper
argon
Titanium
argon
ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
The only routine maintenance required for the power supply is
a thorough cleaning and inspection, with the frequency
depending on the usage and the operating environment.
Warning
Disconnect primary power at the source before removing the
cover. Wait at least two minutes before opening the cover to
allow the primary capacitors to discharge.
To clean the unit, remove the screws securing the outer
cover, lift off the outer cover and use a vacuum cleaner to
remove any accumulated dirt and dust. The unit should also
be wiped clean, if necessary; with solvents that are
recommended for cleaning electrical apparatus.
TROUBLE SHOOTING
TIG welding problems
Weld quality is dependent on the selection of the correct
consumables, maintenance of equipment and proper welding
technique.
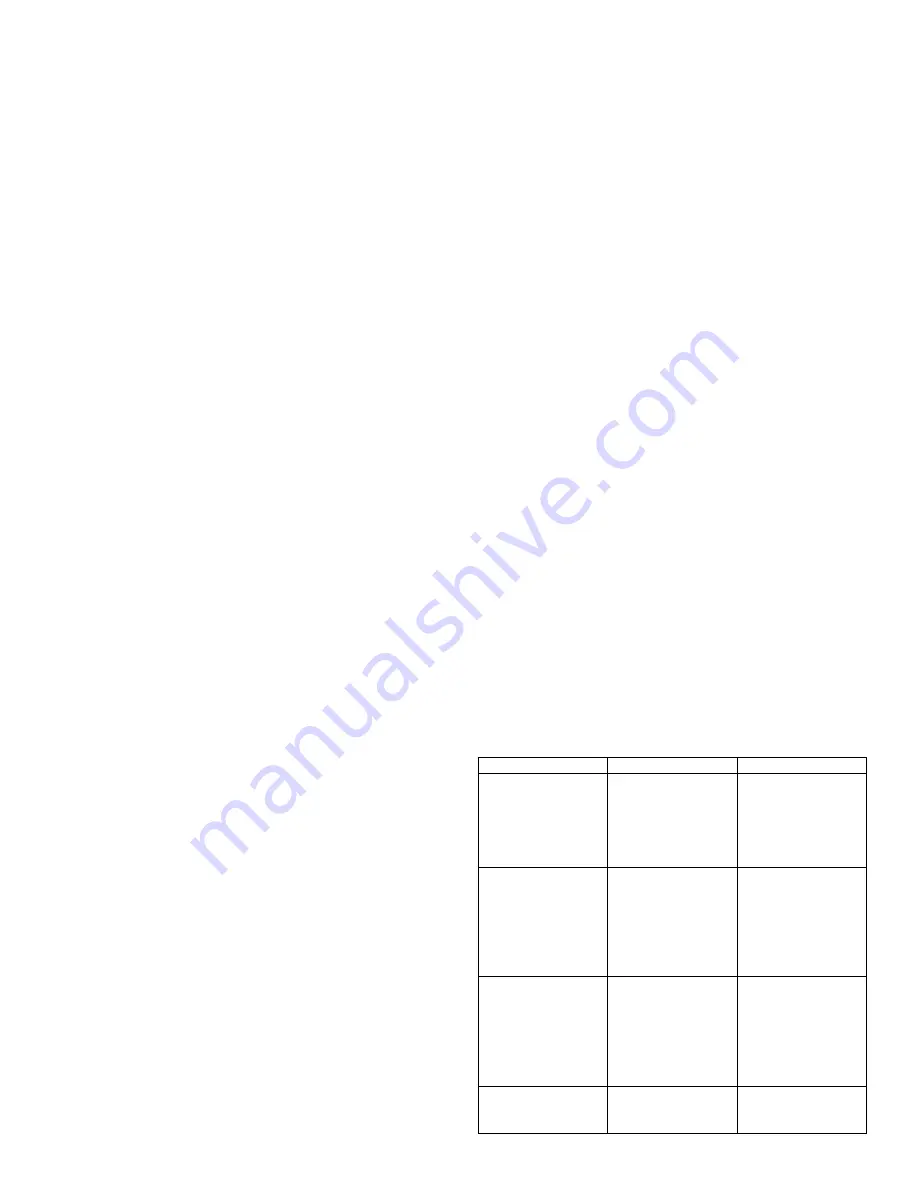
Description Possible
cause Remedy
Excessive bead
build up or poor
penetration or
poor fusion at
edges of weld
Welding current is
too low
Increase weld
current and/or
faulty joint
preparation
Weld bead too
wide and flat or
undercut at edges
of weld or
excessive burn
through
Welding current is
too high
Decrease weld
current
Weld bead too
small or
insufficient
penetration or
ripples in bead are
widely space apart
Travel speed too
fast
Reduce travel
speed
Weld bead too
wide or excessive
bead build up or
Travel speed too
slow
Increase travel
speed


























