Page 8 Instruction manual Parker X-Flow FM-1407 Rev - 11/2021
1.6 Operating Principles
1.6.1 Thermal Gas Flow Sensor Principle
The gas flow sensor operates on a principle of heat transfer by sensing the temperature difference along
a heated section of a capillary tube. Part of the total flow is forced through the capillary by means of a
laminar flow element in the main flow path generating a pressure difference.
The design of the laminar flow device is such that flow conditions in both the capillary and laminar flow
device are comparable, thereby resulting in proportional flow rates through the meter. The amount of
heat absorbed by the gas flow derives the delta-T sensed by the upstream and downstream temperature
sensors on the capillary.
The transfer function between gas mass flow and signal can be described by the equation:
m
p
signal
c
K
V
Φ
⋅
⋅
=
V
signal
= output signal
K = constant factor
c
p
= specific heat
Φ
m
= mass flow
The temperature sensors are part of a bridge circuit. The imbalance is linearized and amplified to the
desired signal level.
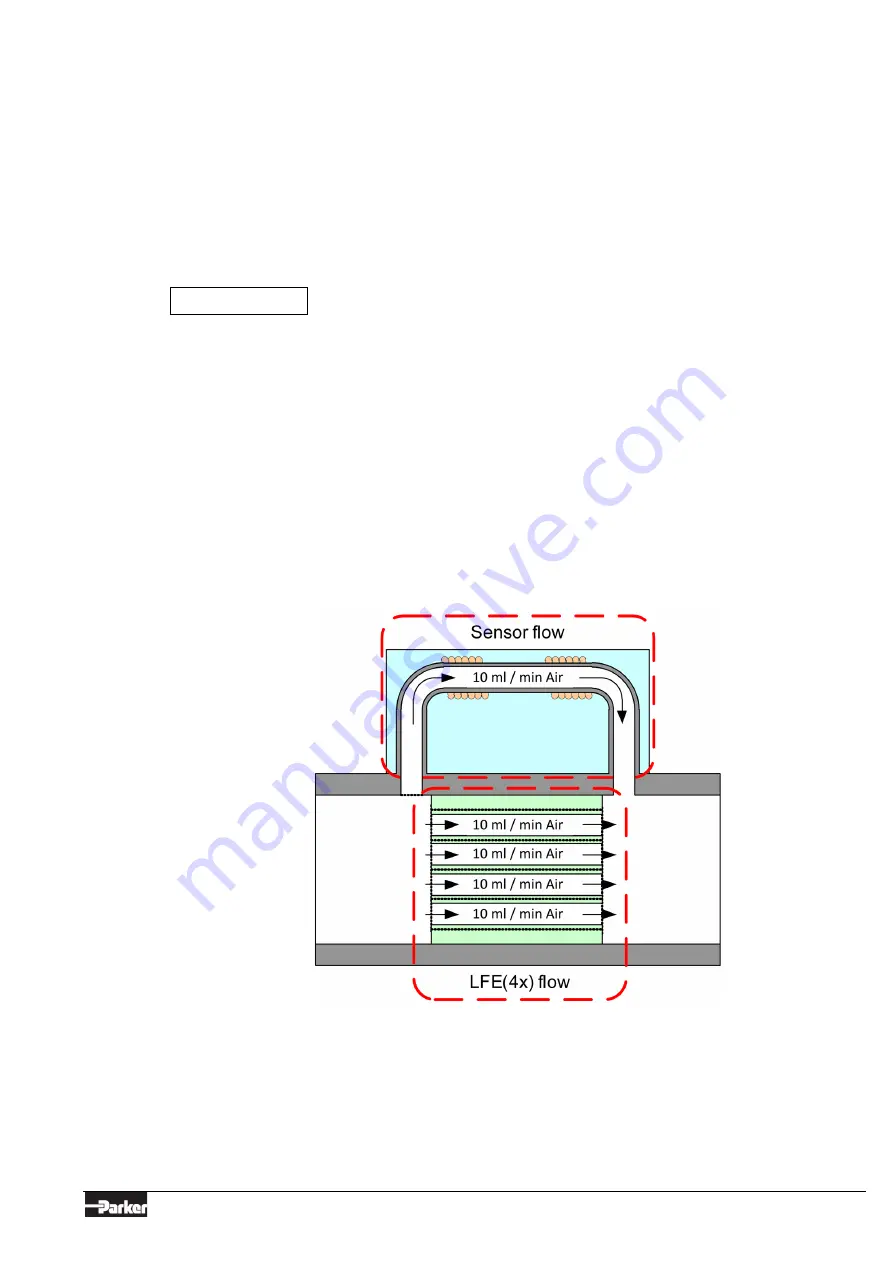
1.6.2 Bypass Principle
The measurement part of an X-Flow™ consists of a thermal sensor and a laminar flow element (LFE). A
laminar flow element consists of a stack of discs with precision etched flow channels. The flow through
each channel is proportional to the flow through the sensor. In this way, by adding more or fewer laminar
flow discs, the total flow rate of an instrument can be adjusted while using the same sensor flow rate.
Example of a 50 ml/min measurement part
Содержание X-Flow FM-1407
Страница 1: ...11 FM 1407...









































