9
Small components like eyepieces and other accessories
should be kept in a protective box or storage case. Keep the
objective lens cap on the front of the telescope when it is not
in use.
Your Observer 60 EQ requires very little mechanical mainte-
nance. The optical tube is aluminum and has a smooth
painted finish that is fairly scratch-resistant. If a scratch does
appear on the tube, it will not harm the telescope. If you wish,
you may apply some auto touch-up paint to the scratch.
Smudges on the tube can be wiped off with a soft cloth and a
household cleaner such as Windex or Formula 409.
cleaning the optics
A small amount of dust or a few specks on the glass objective
(main) lens will not affect the performance of the telescope. If
dust builds up, however, simply blow it off with a blower bulb,
or lightly brush it off with a soft camel-hair brush. Avoid touch-
ing optical surfaces with your fingers, as skin oil may etch
optical coatings.
To remove fingerprints or smudges from a lens, use photo-
graphic-type lens cleaning fluid and lint-free optical lens
cleaning tissue. Don’t use household cleaners or eyeglass-
type cleaning cloth or wipes, as they often contain undesirable
additives like silicone, which don’t work well on precision
optics. Place a few drops of fluid on the tissue (not directly on
the lens), wipe gently, then remove the fluid with a dry tissue
or two. Do not “polish” or rub hard when cleaning the lens, as
this will scratch it. The tissue may leave fibers on the lens, but
this is not a problem; they can be blown off with a blower bulb.
Never disassemble the telescope or eyepieces to clean
optical surfaces!
9. specifications
Objective lens: 60mm-diameter (2.4") achromat, magnesium
fluoride-coated
Focal length: 900mm
Focal ratio: f/15
Eyepieces: 20mm, antireflection coated, .965" barrel diameter
Magnification: 45x (with 20mm eyepiece)
Finder scope: 5x magnification
Diagonal: 90° star diagonal, prism type, .965"
Mount: German-type equatorial
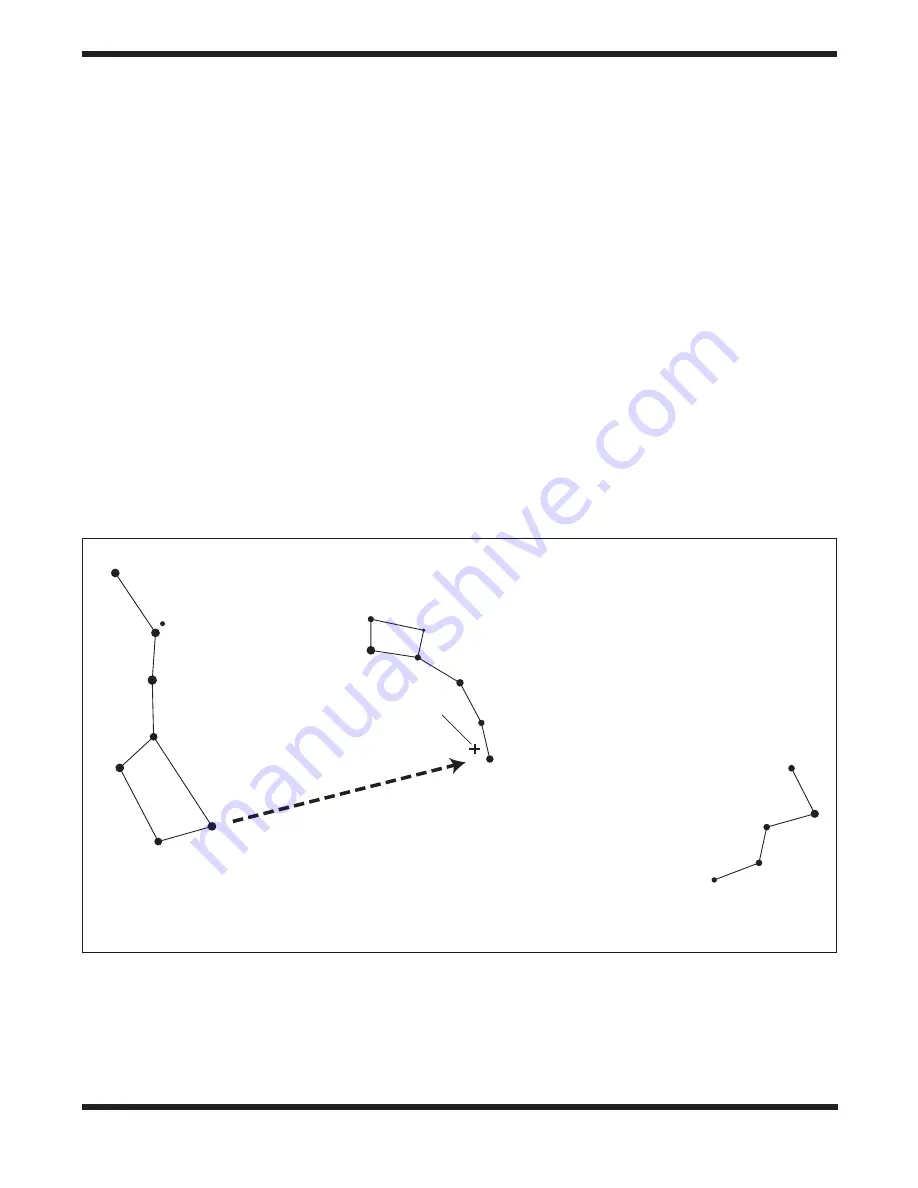
To find Polaris in the night sky, look north and find the Big Dipper. Extend an imaginary line from the two “Pointer Stars” in
the bowl of the Big Dipper. Go about 5 times the distance between those stars and you’ll reach Polaris, which lies within 1°
of the north celestial pole (NCP).
Figure 2
Big Dipper
(in Ursa Major)
Little Dipper
(in Ursa Minor)
N.C.P.
Pointer Stars
Cassiopeia
Polaris










