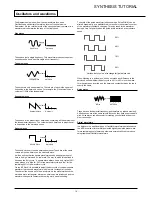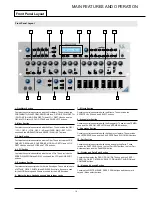
There are more than 128 different parameters that can be transmitted by
MIDI, but because the number of different types of control change mes-
sage is limited to just 128, a a more complicated arrangement had to be
employed for additional parameters.
This method uses what is known as NRPNs. (NRPN stands for Non
Registered Parameter Number). NRPNs consist of three MIDI control
change messages grouped together, rather than a single MIDI control
change message which is used normally.
PITCH BEND MESSAGES
These messages are transmitted whenever the pitch bend wheel is
moved on a Master keyboard.
AFTERTOUCH MESSAGES
These messages are transmitted by some keyboards whenever already-
held down keyboard notes are pressed further. Aftertouch messages can
be used to add extra expressiveness to a sound, for example introducing
an extra vibrato effect.
The MIDI specification defines two different types of aftertouch message;
mono and poly. The type recognised by the KS Rack is mono. Poly after-
touch includes information in the MIDI message about which keyboard
note was used to trigger the aftertouch effect. Poly aftertouch is very
rarely used and only a very few synthesizers ever implemented the sys-
tem.
PROGRAM CHANGE MESSAGES
These messages are transmitted whenever a new sound is selected from
the front panel. The MIDI Specification allows a MIDI program change
message to select one of 128 different sounds. When the MIDI specifica-
tion was originally designed, this was not a problem since synthesizers in
rarely had more than 128 memories.
Modern synthesizers such as the KS Rack offer many more memories, so
it is necessary to send a MIDI program change preceded by an additional
MIDI message which specifies which ‘bank’ of sounds the program
change message will select from.
The bank select MIDI message used for this purpose is a MIDI control
change message (CC32 is the control change number used). Whenever a
new sound is selected, the bank select MIDI message is transmitted, fol-
lowed closely by the appropriate MIDI program change message.
If these messages are then layed back to the KS 4 / KS 5 from a
sequencer, the appropriate sound will be selected.
It is not necessary to send a bank select message before the program
change message (though recommended). It is permitted to omit the bank
select, but if so, the program change message will select the sound from
whatever bank of sounds is currently selected.
Channel Messages
All of these different types of MIDI message detailed above include infor-
mation detailing which MIDI channel was used when the message was
transmitted. MIDI channel messages only affect receiving devices using
the same MIDI channel. For example, a pitch bend message sent using
MIDI channel 1 would have no effect if it were received on a synthesizer
set to respond on MIDI channel 2.
Some MIDI messages do not include any MIDI channel information
defined in them. Some examples of these are :
MIDI CLOCK MESSAGES
These are synchronization messages sent from a sequencer. When
received, they enable tempo-locked features such as the arpeggiator and
various effects parameters (such as Panning and Delay sync) to follow
the current tempo of the sequencer.
The KS Rack itself does not transmit MIDI clock messages, so it can only
be synchronized to follow the tempo of other devices and not vice versa.
Whenever an external sequencer is started, a Start Song MIDI message
is usually transmitted. Certain features can be set to reset their synchroni-
sation when a Start Song message is received.
SYSTEM EXCLUSIVE MESSAGES
This is special type of MIDI message which can contain any type of data,
depending what the synthesizer manufacturer decides to put in it! The
only constraint with system exclusive messages is that they always con-
tain certain header information which is exclusively used by the manufac-
turer (and usually the relevant synth model as well).
This means that a KS Rack will only accept a system exclusive message
designed especially for it. If it receives a system exclusive message trans-
mitted by a different make of synthesizer, the message would simply be
ignored. Similarly, other makes of synthesizer will ignore any system
exclusive messages originally sent by a KS Rack.
System exclusive messages have employed for two distinct purposes.
They can be used to back up all of the Program, Drum Map and
Performance memories and global data. This feature is extremely useful
in building up a sound library on a computer or for making a safety copy
of data in case the worst should happen.
Data backup is discussed in detail on Page 49 in the
Advanced Features
chapter.
System exclusive messages also enable an entire new operating system
to be received via MIDI. The latest operating system is always available
free of charge at the Novation web site. From there, it can be downloaded
as an SMF (Standard MIDI File).
Because the operating system update consists purely of MIDI system
exclusive messages, it can then be transferred by playing the file on a
sequencer directly into the machine. However, as a safety feature, the KS
Rack must be set to a special mode where it is able to accept an operat-
ing system update. Full details on how to do this are supplied along with
the downloaded OS update.
For a list of the latest operating system updates, please visit the Novation
website :
http://www.novationmusic.com
A MIDI Implementation Chart provides a concise way of telling at a glance
which MIDI messages an instrument will transmit and respond to. A MIDI
Implementation Chart for the KS Rack can be found on page 57. How it
transmits and responds to MIDI in the different playing modes is also
described in detail on page 56.
MIDI TUTORIAL
MIDI messages
•
16
•