N500-79-00
5
I56-1805-012
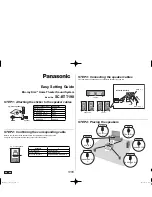
Figure 9: Example of Class B, Style Y NAC configuration with a single supply dedicated to a single NAC.
BASE ADDRESS
STATUS
INDICATORS
NAC
PS
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
TO
P
BOT
– +
+
NA
C
–
– +
–
PS
+
SLC
PS
—
+
+
—
+1
+2
+3
+4
+5
T1
1
T10
T0
+0
T12
T1
T2
T3
T4
T5
T13
T14
T15
T16
ENABLE POWER SUPPL
Y
MONIT
OR
DISABLE SHO
R
T
CIRCUIT
PROTECTION
—
+
+
—
A/B SELECT
DISABLE 1
DISABLE 2
DISABLE 3
0
1
2
3
4
5 6
7 8 9
0
7 8
6
5
4
3
2
1
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
EXTERNAL
POWER
SUPPLY
TO NEXT
DEVICE
–
+
–
+
FROM PANEL OR
PREVIOUS DEVICE
–
+
–
+
SIGNAL LINE CIRCUIT (SLC) 32 VDC MAX.
SEE PANEL INSTRUCTION MANUAL
FOR WIRE REQUIREMENTS.
(–)
(+)
POWER-LIMITED
AND SUPERVISED
TOP OF T0
EOLR-1
A2143-10
RED
VIO
VIO
RED
BLK
BLK
(–)
(+)
+
–
47K
NOTE:
EOL RELAY COIL CONNECTIONS MUST BE MADE USING
EOL RELAY CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES ON T10-T16 IN EVENT
THAT ALL NACS ON THE PCB HAVE DEDICATED SUPPLIES.
C0816-02
external supply connection points, at T0–T5, are marked by PS–
and PS+ on the PCB legend. Pin 1 is indicated by a dot next to
T10–T16. The odd pins, on T10–T16, always connect to PS– pins
(e.g. PS–, of the +0 NAC, is connected to T10–1 and T11–1). The
even pins always connect to PS+ pins (e.g. PS+, of the +5 NAC,
is connected to T15-4 and T16-2).
TABLE 3
PS OR NAC NUMBER (TERMINAL / PINS)
TERMINAL / PINS
+0 (T0 – BOTTOM / PS- & PS+)*
T10 / 1 & 2, T11 / 1 & 2
+1 (T1 / PS- & PS+)
T11 / 3 & 4, T12 / 1 & 2
+2 (T2 / PS- & PS+)
T12 / 3 & 4, T13 / 1 & 2
+3 (T3 / PS- & PS+)
T13 / 3 & 4, T14 / 1 & 2
+4 (T4 / PS- & PS+)
T14 / 3 & 4, T15 / 1 & 2
+5 (T5 / PS- & PS+)
T15 / 3 & 4, T16 / 1 & 2
*Note: T0–TOP is reserved for SLC connections only (see Figure 8).
All power supplies, external to the cabinet (in which the XP6-C is
housed), should be connected to T0–T5 which are suitable con-
nectors for field wiring. The 1 x 4 terminal blocks, shown on page
1, should be used to make these connections.
All NACs can be wired to be powered by separate external sup-
plies (figures 9 and 11 are typical), or a single supply (figures 10
and 12 are typical) can be shared among multiple NACs. If a sup-
ply is to be shared, between NACs wired to a common PCB, use
the short power supply jumpers shown on page 1. The jumpers
can be used on T11–T15. Refer to Table 4 for jumper functions.
When multiple (2 or more) NAC circuits share a power supply,
the wiring for the power supply must be in conduit and 20 feet
or less from the XP6-C board.
TABLE 4
JUMPER LOCATION
NAC PAIR SHARING SUPPLY
T11*
+0 and +1
T12
+1 and +2
T13*
+2 and +3
T14
+3 and +4
T15*
+4 and +5
*NOTE:
Jumpers must be placed on T11, T13 and T15 for all Class
A, Style Z applications.
A supply can be wired to be shared among multiple PCBs in the
same cabinet (figure 15 is typical). To share among multiple PCBs:
use the long power supply jumpers (shown on page 1) to connect
either T10 or T16, of one PCB, to either T10 or T16 of the other
PCB..
An EOL relay must be used for every external power supply
(figures 9–12 are typical). The EOL relay coil should always be
connected at the external power supply input of the module
which is connected to the ends of the wires which are farthest
from the power supply. The EOL relay contacts should always be
connected in series with the NAC wiring of the same module. The
EOL relay coil should be connected across the PS+ (red wire) and
PS- (black wire) if it is connected at T0 – T5. The EOL relay coil
should be connected across adjacent pins (red – even pin#, black
– odd pin#), of the same connector, if T10 – T16 are used. If the
supply is an audio amplifier then the points, where the EOL relay
coil would normally be connected, should be connected to the
amplifier supervision EOL device (figures 13 and 14 are typical).
All wiring must be in accordance with the NEC, NFPA 72 and all
other applicable codes and standards. All external power supplies
must be voltage regulated with battery back-up. All external power
supplies, audio amplifiers, EOL relays, and notification appliances
must be UL listed for fire protection signaling applications.