8
330
Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4.0 Reference Guide
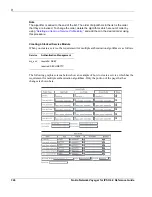
In tunnel mode, the original IP datagram is placed inside a new datagram, and AH or ESP are
inserted between the IP header of the new packet and the original IP datagram. The new header
points to the tunnel endpoint, and the original header points to the final destination of the
datagram. Tunnel mode offers the advantage of complete protection of the encapsulated
datagram and the possibility to use private or public address space. Tunnel mode is meant to be
used by routers—gateways. Hosts can operate in tunnel mode too.
With IPSec tunnel mode:
If AH is used, the outer header is authenticated as well as the tunneled packet:
If ESP is used, the protection is offered only to the tunneled packet, not to the new outer IP
header. By default, ESP, providing the highest level of confidentiality, is used in this release.
Building VPN on ESP
Tunneling takes the original IP header and encapsulates it within ESP. Then it adds a new IP
header, containing the address of a gateway, to the packet. Tunneling allows you to pass
nonrouteable and private (RFC 1918) IP addresses through a public network that otherwise
would not be accepted. Tunneling with ESP using encryption also has the advantage of hiding
the original source and destination addresses from the users on the public network, reducing the
chances of traffic analysis attacks. Tunneling with ESP can conceal the addresses of sensitive
internal nodes, protecting them from attacks and hiding its existence to outside machines.
Protocol Negotiation and Key Management
To successfully use the IPSec protocol, two gateway systems must negotiate the algorithms used
for authentication and encryption. The gateway systems must authenticate themselves and
choose session keys that will secure the traffic. The exchange of this information leads to the
creation of a security association (SA). An SA is a policy and set of keys used to protect a one-
New IP header
AH
Old IP
header
Payload
New IP header
ESP header
Old IP
header
Payload
ESP trailer
ESP auth
New IP header
AH
Old IP header
Authenticated
Payload
00128
New IP header
ESP header
Old IP header
Authenticated
Payload
00129
ESP trailer
ESP auth
Encrypted
Содержание IPSO 4.0
Страница 1: ...Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4 0 Reference Guide Part No N451818001 Rev A Published October 2005 ...
Страница 4: ...4 Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4 0 Reference Guide ...
Страница 182: ...3 182 Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4 0 Reference Guide ...
Страница 206: ...4 206 Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4 0 Reference Guide ...
Страница 248: ...5 248 Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4 0 Reference Guide ...
Страница 266: ...6 266 Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4 0 Reference Guide ...
Страница 286: ...7 286 Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4 0 Reference Guide ...
Страница 350: ...8 350 Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4 0 Reference Guide ...
Страница 478: ...11 478 Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4 0 Reference Guide ...