Chapter 2
Using the Module
©
National Instruments Corporation
2-23
I/O Connector Signal Description
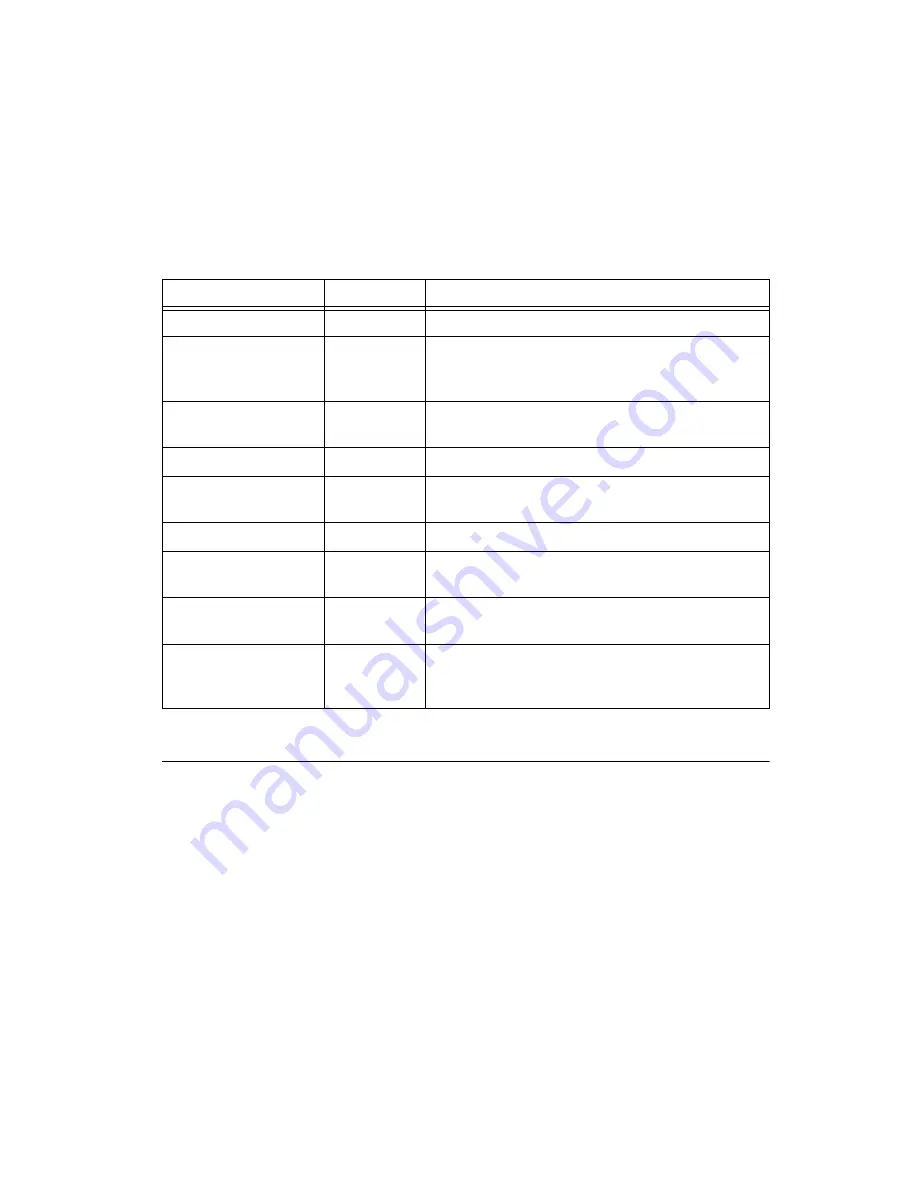
Table 2-2 describes the signals found on the I/O connector.
NI PXIe-4330/4331 Block Diagram
Figure 2-18 shows the analog input circuitry block diagram of the NI PXIe-4330/4331.The
programmable excitation block provides the excitation voltage for the bridge or sensor. The
voltage level is configurable on a per channel basis. This excitation voltage is sensed locally
or remotely via the remote sense terminals (RS+ and RS–) and fed back to the ADC
(Analog-to-Digital Converter) reference through a programmable gain amplifier. The gain
applied when sensing the excitation voltage is automatically selected based on the selected
excitation voltage level.
Table 2-2.
I/O Connector Signal Descriptions
Signal Names
Direction
Description
AIGND
—
Analog Input Ground
AI<0..7>+, AI<0..7>–
Input
Analog Input Channels 0 to 7—AI+ and AI– are the
positive and negative inputs of the differential analog
input.
QTR/SC<0..7>
—
These pins provide the connection point for
quarter-bridge completion and shunt calibration.
EX<0..7>+, EX<0..7>–
Output
Provides the differential bridge excitation voltage.
RS<0..7>+, RS<0..7>–
Input
Remote sense input. The remote sense pins sense the
actual voltage applied to the bridge.
T<0..7>+
Input/Output
TEDS sensor digital communication lines.
T<0..7>–
—
Negative reference for TEDS communication.
Internally connected to the module digital ground.
RSVD
—
These pins are reserved for communication with the
accessory.
DGND
—
Digital ground—these pins supply the reference for
module digital signals and are connected to the module
digital ground.
















































