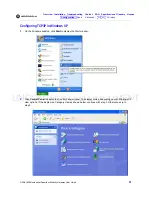
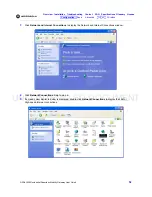
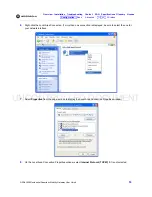
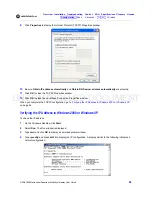
UNCONTROLLED DOCUMENT
Overview Installation Troubleshooting
Basic Advanced TCP/IP Wireless
RSGu3500 Residential Seamless Mobility Gateway User Guide
102
Glossary
This glossary defines terms and abbreviations used in this manual.
10/100Base-T
See
Ethernet
.
adapter
A device or card that connects a computer, printer, or other peripheral device to the network or to
some other device. An Ethernet adapter connects a computer to the LAN.
broadband
High-speed telecommunication over a wide range of frequencies, typically 256 Kbps or faster.
Broadband enables more information to be transmitted in less time. The most common broadband
service types available to homes and small-offices are cable modem and DSL. Both cable modem
and DSL are much faster than a traditional dial-up Internet connection.
broadband
provider
If you have a cable modem, the cable company from which you subscribe to high-speed data
service. If you have a DSL modem, the telephone company from which you subscribe to DSL
service.
cable modem
A device enabling a broadband connection to the Internet over cable television lines. It requires a
subscription for high-speed data service from your local cable provider.
coaxial cable
(coax)
A type of wire consisting of a center wire surrounded by insulation and a grounded shield of braided
wire traditionally used mainly to carry cable television signals. The shield minimizes electrical and
radio frequency interference.
default gateway
A designated router that forwards all traffic not addressed to a host on the local subnet.
DHCP
A Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server dynamically assigns IP addresses to client hosts on
an IP network. DHCP eliminates the need to manually assign static IP addresses by “leasing” an
IP address and subnet mask to each client. It enables the automatic reuse of unused IP addresses.
The RSGu3500 can simultaneously be a DHCP client and a DHCP server:
•
A DHCP server assigns a WAN IP address to your RSGu3500.
•
The RSGu3500 contains a built-in DHCP server that assigns private IP addresses to each
computer on its LAN.
DMZ
A “de-militarized zone” is one or more
logically located between a private LAN and the
Internet. A DMZ prevents direct access by outside users to private data. (The term comes from the
geographic buffers located between some conflicting countries such as North and South Korea.) In a
typical small DMZ configuration, the DMZ host receives requests from private LAN users to access
external web sites and initiates sessions for these requests. The DMZ host cannot initiate a session
back to the private LAN. Internet users outside the private LAN can access only the DMZ host. You
can use a DMZ to set up a web server or for gaming without exposing confidential data.
DOCSIS
The Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specification define a standard interface for cable modems
to deliver data between a cable network and computer systems. Euro-DOCSIS is DOCSIS adapted
for use in Europe.
DNS
The Domain Name System is the Internet system for converting domain names to IP addresses. A
DNS server contains a table matching domain names such as Internetname.com to IP addresses
such as 192.169.9.1. When you access the Web, a DNS server translates the URL displayed on the
browser to the destination website IP address. The DNS lookup table is a distributed Internet
database; no one DNS server lists all domain-to-IP address matches.
domain name
A unique name, such as motorola.com, that maps to an IP address. Domain names are typically
much easier to remember than IP addresses.
dotted-decimal
format
Method of representing an IP address or subnet mask using four decimal numbers called octets.
Each octet represents eight bits.
In a class C IP address, the octets are “network.network.network.host.” The first three octets
together represent the network address and the final octet is the host address. In the RSGu3500
LAN default configuration, 192.168.15 represents the network address. In the final octet, the host
address can be from 2 to 254.
download
To copy a file from one computer or other network device to another. You can use the Internet to
download files from a server to your home computer. Your residential gateway downloads its
configuration file and firmware.