0
Development System EasydsPIC6
MikroElektronika
page
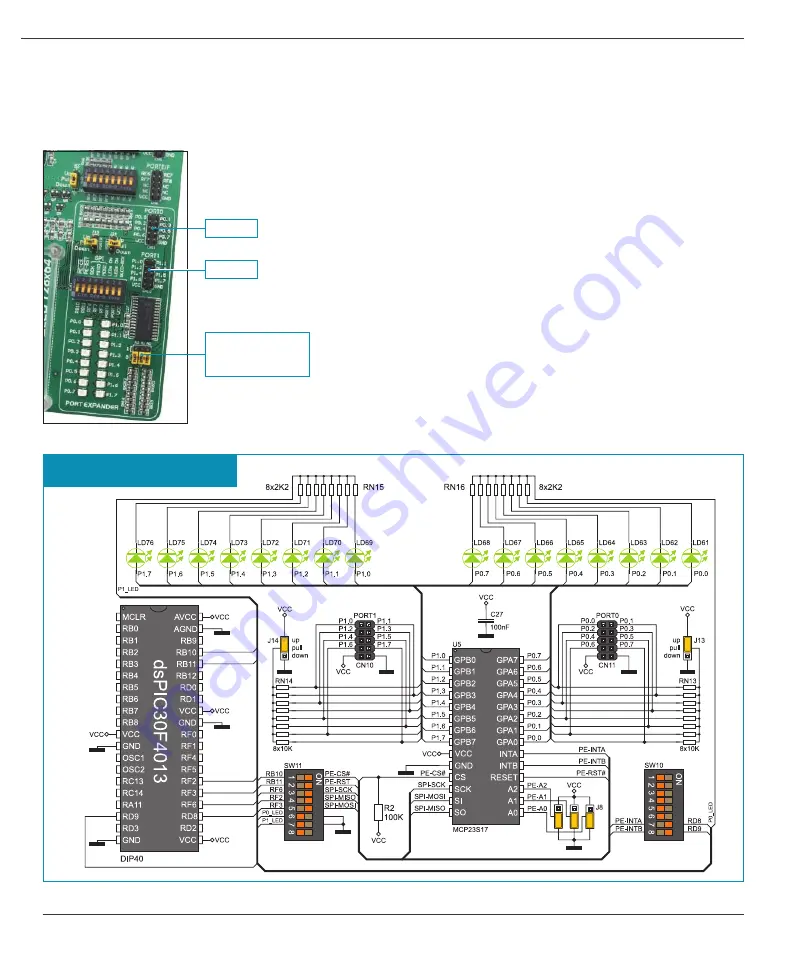
23.0. Port Expander (Additional Input/Output Ports)
SPI communication lines and MCP23S17 circuit provide the
EasydsPIC6
development system with means of increasing the number of
available I/O ports by two. If the port expander communicates to the microcontroller over the DIP switch SW11 then the microcontroller
pins RB10, RB11, RF6, RF2 and RF3 used for the operation of port expander, cannot be used as I/O pins.
Figure 23-2
: Port expander and microcontroller connection schematic
Figure 23-1
: Port expander
PORT0
Jumper for selecting
pull-up/pull-down re-
sistor
The microcontroller communicates with the port expander (MCP23S17 circuit)
using serial communication (SPI). The advantage of such communication is that
only five lines are used for simultaneous data transceive and receive:
MOSI
- Master Output, Slave Input (microcontroller output, MCP23S17 input)
MISO
- Master Input, Slave Output (microcontroller input, MCP23S17 output)
SCK
- Serial Clock (microcontroller clock signal)
CS
- Chip Select (enables data transfer)
RST
- Reset
Data transfer is performed in both directions simultaneously by means of MOSI and
MISO lines. The MOSI line is used for transferring data from the microcontroller to
the port expander, whereas the MISO line transfers data from the port expander
to the microcontroller. The microcontroller initializes data transfer by sending a
clock signal when the CS pin is driven low (0V). The principle of operation of the
port expander’s ports 0 and 1 is almost identical to the operation of other ports
on the development system. The only difference here is that port signals are
received in parallel format. The MCP23S17 converts then such signals into serial
format and sends them to the microcontroller. The result is a reduced number of
lines used for sending signals from ports 0 and 1 to the microcontroller.
DIP switch SW11 enables port
expander
PORT1



































