5.
FAQs, Tips, and Troubleshooting
5.1
FAQs and Tips
1. How can the user change the Wi-Fi configuration?
There are four ways to do it:
1.
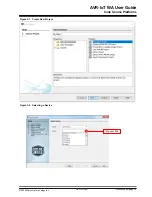
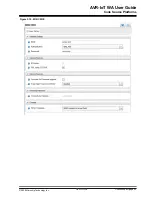
Connect to the USB and click the ‘
click-me
’ file to reach the dedicated page for the device and enter the
new credentials in the web form. Download the resulting file to the CURIOSITY drive. Read more in Section
.
2.
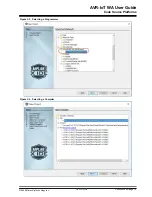
Connect to the USB and open a serial port terminal (Windows users will need to install serial port drivers).
From the command line, use the
Wi-fi
.
3.
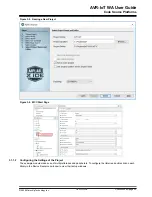
Press the
SW0
button while powering up the board and the WINC will turn to Access Point mode. Connect the
laptop or phone to it and fill in the online form. See Section
2.3 Connecting the Board to Wi-Fi Networks
for
details.
4.
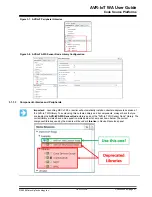
Use MCC to re-build the project after changing the default Wi-Fi configuration in the WINC module.
Reprogram the board using MPLAB X or drag and drop the new image to the CURIOSITY drive. Further
details can be found in Section
.
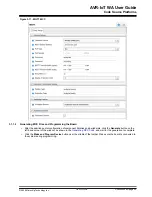
2. How can the user change the Wi-Fi credentials using the online form without exposing the details to
security threats?
Although it appears in the browser, the Wi-Fi credential setup form does not transfer any information to third parties.
A small text file (WIFI.CFG) is created (this can also be done manually using any text editor) and it is recommended
that saves it directly to the CURIOSITY drive. Since the browser settings vary according to the platform and personal
preferences, the user might have to change them or perform a drag and drop from the default download folder. Even
though it looks like the WIFI.CFG file is now stored on the CURIOSITY drive, this is just an artifact of the operating
system (caching). No file is permanently recorded and the information contained is immediately used to update the
Wi-Fi module settings. These settings will be maintained after subsequent power cycles of the AVR-IoT Development
Board, but the file will disappear.
3. Can a phone/tablet alone be used to perform the demo?
Assuming the user has a way to provide power to the board (a USB back-up battery, a USB charger, a Li-Ion battery,
or other 3.3V-5V power supply), the QR code can be scanned (on a sticker under the board, next to the Microchip
and Amazon color logos) using any smartphone camera (old operating system versions might still require a separate
app) and open the resulting link in the smartphone browser.
4. The user scanned the bar code with the phone/tablet, but nothing happened?
Ensure the scanning of the QR code present on the sticker under the AVR-IoT WA board. It can be recognized by the
distinguishing squares on the three of its corners and its proximity (same sticker) to the MCHP and Amazon logos (in
color). Although there are also other bar codes present on the Wi-Fi module, and/or the anti-static bag the board
came with, those are not QR codes.
5. Which battery is recommended to be used with the AVR-IoT WA Sensor Node board?
Microchip recommends Li-Ion or Li-Poly batteries with at least 400 mAh capacity and 3.7V nominal. For more
information about powering the board, refer to the
AVR-IoT Wx Hardware User Guide.
Other Helpful Tips:
The following steps are not required for operating the AVR-IoT WA Sensor Node board, but will significantly increase
the possibility of positive results.
1.
Get a USB cable with all the four wires connected
. There are a lot of non-compliant USB cables available
that provide only 5V power (two wires). How can the user verify it? Plug the board into the laptop and check in
the File Manager (Finder) for the presence of a new hard drive (named CURIOSITY). If it fails to pop up after a
second or two, the cable is not the appropriate one.
2.
Prepare the Wi-Fi router for the demo
. The easiest way to go is to set up the phone as a hotspot. The
following credentials should be used, name (SSID):
MCHP.IOT
and password:
microchip
(
WPA 2
is assumed,
AVR-IoT WA User Guide
FAQs, Tips, and Troubleshooting
©
2020 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002998A-page 27