12
LT1425
APPLICATIO
N
S I
N
FOR
M
ATIO
N
W
U
U
U
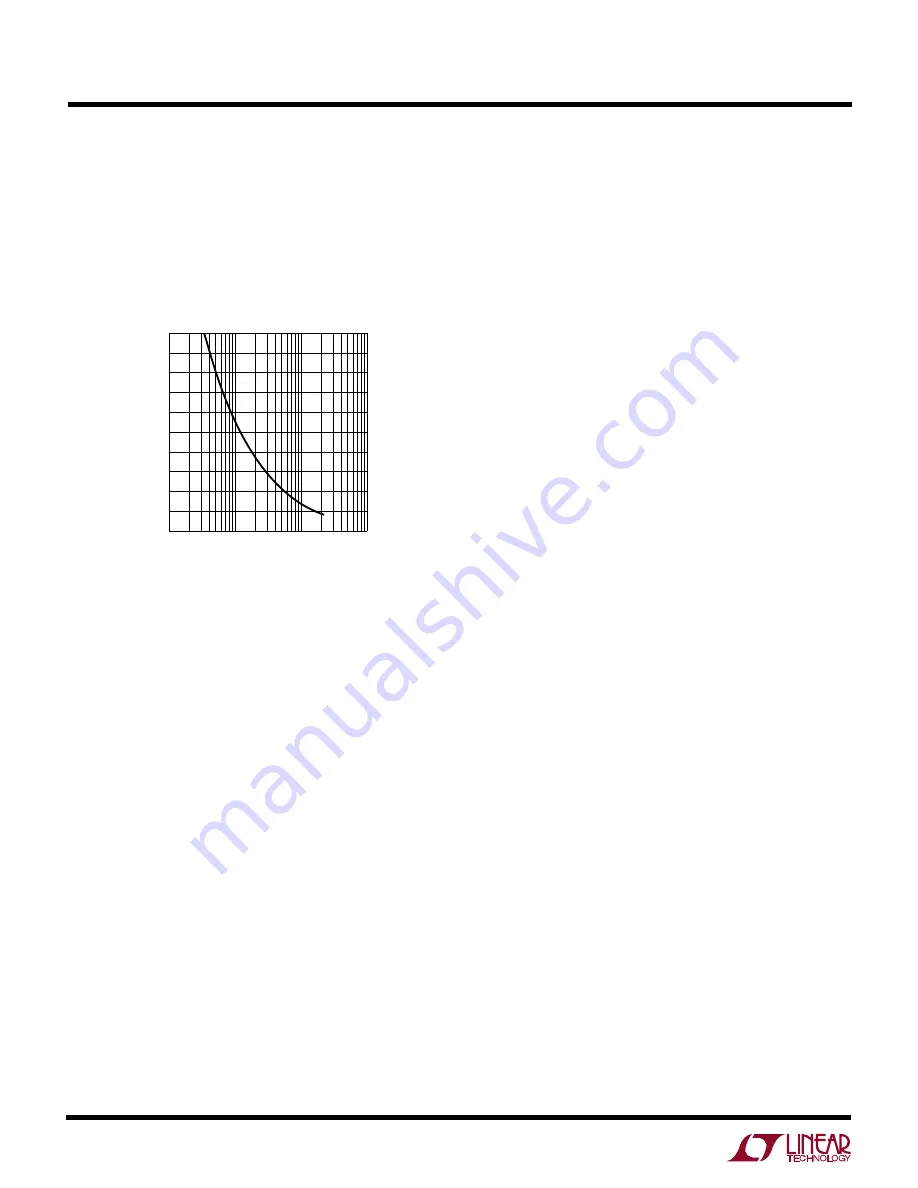
amount when output switch current is zero. Please refer
to Figure 1 which shows nominal reference current shift
at zero load for a range of R
OCOMP
values. Example: for
a load compensation resistor of 12k, the graph indi-
cates a 1.0% shift in reference current. The R
FB
resistor
value should be adjusted down by about 1.0% to
restore the original target output voltage.
integers, e.g., 1:1, 2:1, 3:2, etc. can be employed which
yield more freedom in setting total turns and mutual
inductance. Turns ratio can then be chosen on the basis of
desired duty cycle. However, remember that the input
supply voltage plus the secondary-to-primary referred
version of the flyback pulse (including leakage spike) must
not exceed the allowed output switch breakdown rating.
Leakage Inductance
Transformer leakage inductance (on either the primary or
secondary) causes a spike after output switch turn-off.
This is increasingly prominent at higher load currents
where more stored energy must be dissipated. In many
cases a “snubber” circuit will be required to avoid over-
voltage breakdown at the output switch node. LTC’s
Application Note 19 is a good reference on snubber
design.
In situations where the flyback pulse extends beyond the
enable delay time, the output voltage regulation will be
affected to some degree. It is important to realize that the
feedback system has a deliberately limited input range,
roughly
±
50mV referred to the R
REF
node, and this works
to the user’s advantage in rejecting large, i.e., higher
voltage leakage spikes. In other words, once a leakage
spike is several volts in amplitude, a further increase in
amplitude has little effect on the feedback system. So the
user is generally advised to arrange the snubber circuit to
clamp at as high a voltage as comfortably possible,
observing switch breakdown, such that leakage spike
duration is as short as possible.
As a rough guide, total leakage inductances of several
percent (of mutual inductance) or less may require a
snubber, but exhibit little to no regulation error due to
leakage spike behavior. Inductances from several percent
up to perhaps ten percent cause increasing regulation
error.
Severe leakage inductances in the double digit percentage
range should be avoided if at all possible as there is a
potential for abrupt loss of control at high load current.
This curious condition potentially occurs when the leak-
age spike becomes such a large portion of the flyback
waveform that the processing circuitry is fooled into
thinking that the leakage spike itself is the real flyback
In less critical applications, or when output current
remains relatively constant, the load compensation func-
tion may be deemed unnecessary. In such cases, a
reduced component solution may be obtained as follows:
Leave the R
OCOMP
node open (R
OCOMP
=
∞
), and replace
the filter capacitor normally on the R
CCOMP
node with a
short to ground.
TRANSFORMER DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Transformer specification and design is perhaps the most
critical part of applying the LT1425 successfully. In addi-
tion to the usual list of caveats dealing with high frequency
isolated power supply transformer design, the following
information should prove useful.
Turns Ratio
Note that due to the use of an R
FB
/R
REF
resistor ratio to set
output voltage, the user has relative freedom in selecting
transformer turns ratio to suit a given application. In other
words, “screwball” turns ratios like “1.736:1.0” can scru-
pulously be avoided! In contrast, simpler ratios of small
R
OCOMP
(k
Ω
)
1
∆
I
REF
(%)
2
10
100
1000
1425 F01
1
0
Figure 1






































