15
(15190) PreLOG
Operating Instructions
Operating Instructions
Data Logger PreLOG (15190)
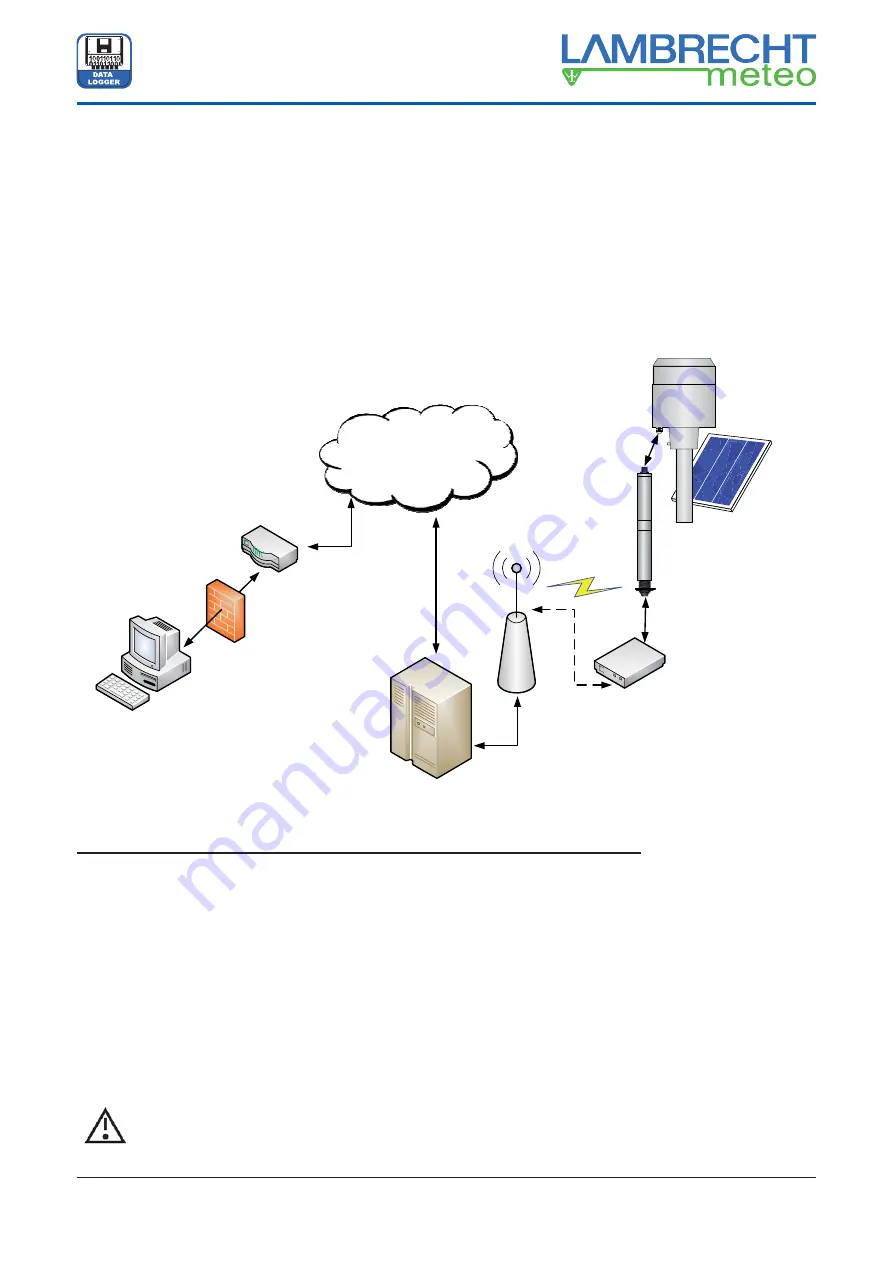
Remote Send (GPRS)
The COM1 interface (with connected modem) will be activated by the PreLOG in speci
fi
ed intervals or to transmit
triggered alarm messages. Then a packet oriented connection to an appropriate MeteoWare host with static IP
address will be established via GPRS.
All data which have not been sent previously, will be transmitted automatically by the PreLOG. It recalls the last
transmitted data set and starts the next transmission with the following data set. If there are no recent data avail-
able, the record “
NoData
” will be transmitted.
After a successful data transmission the interface and the modem will be deactivated.
This type of communication is most suitable for application with limited power supply e. g. solar powered precipita-
tion stations. Please note the respective connecting diagram (Fig. 9, p. 8).
Additional remark for the recommended communication mode „Remote Send“:
The MeteoWare host must be accessible via internet on an invariable address (hostname/IP address). Either with
a static IP address (for example a company network with a
fi
x connection to the internet via
fi
rewall) or, in case
of a dial up connection (DSL), via a so called Dynamic Hostname Service: A well-known example (among others)
is DynDNS. Such a dynamic DNS service automatically maps between the volatile IP address of the router (that
will change on every dial up, but at the latest once a day) and a
fi
x hostname.
Remote Send / Request (GPRS/GSM)
The COM1 interface and a connected modem are permanently activated. Requests can be made as in the com-
munication type Remote Request. In the speci
fi
ed interval or in case of alarms the PreLOG will transmit data as
in the communication type Remote Send.
Since the COM1 and the modem are permanently activated and consume energy in this type of communication,
its suitability is limited for applications with solar power supply.
Attention! If the mode
“
Remote Send / Request
”
is used, the PreLOG will terminate a possibly exist-
ing connection and thereby any ongoing data transmission of a Request process and establishes
a new connection to execute the Send process on time.
:::&ORXG
)LHOGVWDWLRQ
2IILFH3&
3URYLGHU
FHOOSKRQH
'6/9'6/
5RXWHU
)LUHZDOO
5XQQLQJ0HWHR:DUH5DLQ
IRUZDUGLQJ
SRUW
DVSHFLDO$SSUXQQLQJDV
:LQGRZV6HUYLFHLVUHFHLYLQJ
GDWDIURP3UH/2*DQGVWRUHV
WKHPLQWR0HWHR:DUHGDWDEDVH
*3560RGHP
3UH/2*
3UHFLSLWDWLRQ
6HQVRU
6RODUSDQHO
SOXVFKDUJHU
DQGEDWWHU\
FRQILJXUHG
WRVHQGLWV
GDWDWRD3&
YLD*356
PRGHP
WKHFRPPXQLFDWLRQLV
VWDUWHGE\3UH/2*RQO\
&RPPXQLFDWLRQ3UH/2*± 3&
YLD5HPRWH6HQG*356
UHFHLYHVGDWDSDFNDJHVZLWKLVWEDVHWUDQVFHLYHUVWDWLRQ
DQGVHQGVWKHPYLD,QWHUQHWWRWKH0HWHR:DUH+RVW3&
Fig. 13













































