16
| SOLARIS SYNTHESIZER
Algorithm
Description
Clip
Multiplies the two input signals and
clips the result. Creates two strong
sidebands (stronger than those gen-
erated by Shift) around the carrier's
frequency, and on strong sideband
at a much lower frequency. Phase
cancellation eliminates the original
carrier.
Abs (abso-
lute)
Outputs the absolute value of multi-
plying the two input signals without
clipping. Creates two weak sidebands
widely spaced around the carrier.
Ring
Classic ring modulation that creates
two strong sidebands around the
carrier and eliminates the carrier com-
pletely due to phase cancellation.
AM
Table 7:
Algorithms
With certain combinations, you will get identical results for
some of these algorithms, depending on the position of A
and B (A x B, or B x A, or which is the modulator and which the
carrier).
Using waveforms other than sine waves will result in addi-
tional sidebands for each frequency component of the carrier,
which allows very complex waveforms to be generated.
X Mult (multiplier)
These are four identical circuits that can be used to
multiply an input signal by itself, using ring modula-
tor modules. This technique can be used to produce
extremely exaggerated, or “exponentiated”, control sig-
nals, such as the old DX7 trick of running an envelope
into both inputs of a ring modulator (a multiplier) to get
an exaggerated taper and long decay time on the en-
velope. Note that this technique does not work well with
Attack times. The x Mults on Solaris 5 also allows you
to cross fade between the original and the multiplied
output, giving very
fi
ne control over the slope shape.
Another use for the x Mults is generating organ-like
sounds by generating multiple octaves of sine waves.
By using a sine wave as the input to both x Mults, you
can generate octaves above the source by taking the
output and multiplying it again and again, for the dif-
ferent octaves. The Mult Factor control allows you to
specify how many times the signal is multiplied.
The x Mult sections consist of:
The input selection (Source)
•
The number of times you multiply the signal by itself
•
(Mult Factor)
The (X-Fade Amt) amount the ‘dry’ signal and the
•
‘multiplied’ signals will be cross faded
Factor Eff ect
1
Source goes to both inputs
2
Source goes to 1 input, with the output of the
fi
rst ring mod mult to the second input
3
Source goes into one input, with the output of
the factor 2x into the second input
4
Source goes into one input, with the output of
the factor 3x into the second input
5
Source goes into one input, with the output of
goes factor 4x into the second input
Effect of the xMult Factor setting
Table 8:
Solaris allows many diff erent signal sources to act as carrier
and modulator for AM synthesis. Table 7 describes the eff ect of
each AM algorithm in terms of a sinusoidal carrier modulated
by a sine wave. Since sine waves are the least harmonically
rich waveforms, it is easier to understand the functions of AM
synthesis using them as examples.
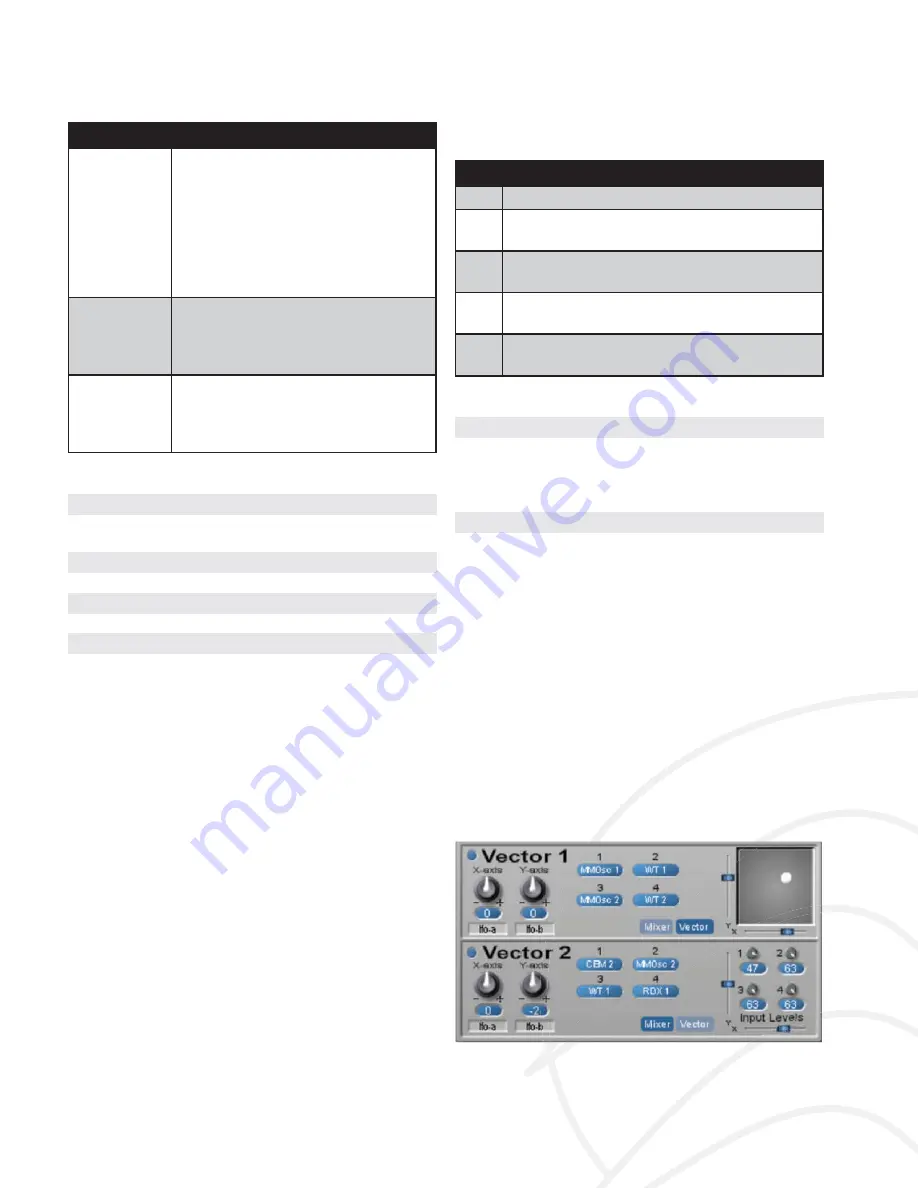
Vector Synthesis
(Vector)
The Vector Synthesis section allows four different
sound sources to be mixed/morphed dynamically
based on a 2 dimensional x/y vector graph. Vector
Synthesis allows Solaris to achieve swirling, moving
dynamic sounds reminiscent of the Sequential Circuits
Prophet VS. Each corner of the control represents the
full level of one of the four input sources. The joystick
control can be assigned to a hardware MIDI controller
or modulated by any of Solaris’ extensive modulation
sources.
This section has two pages selectable with the Mixer/
Vector buttons:
Figure 16: Vector and Mixer controls
Like the Rotor, the Vector mixer has four inputs, each of
which can be selected from a very long list of sources
(see below). Like all mixers in the Solaris (and identi-
cal to the Rotors), each input also has a bipolar Level
Содержание Solaris V5
Страница 1: ...User Guide V5 By John Bowen and Brent Garlow ...
Страница 30: ...30 SOUND MODIFIERS Figure 35 Looping Envelope Diagram ...
Страница 47: ...John Bowen Synth Design www johnbowen com ...