15
Accessing ViewCommander-Edge Remotely
This example illustrates how to remotely access ViewCommander-NVR located on a private network. This example can
also be applied to remotely accessing IP cameras located on private networks.
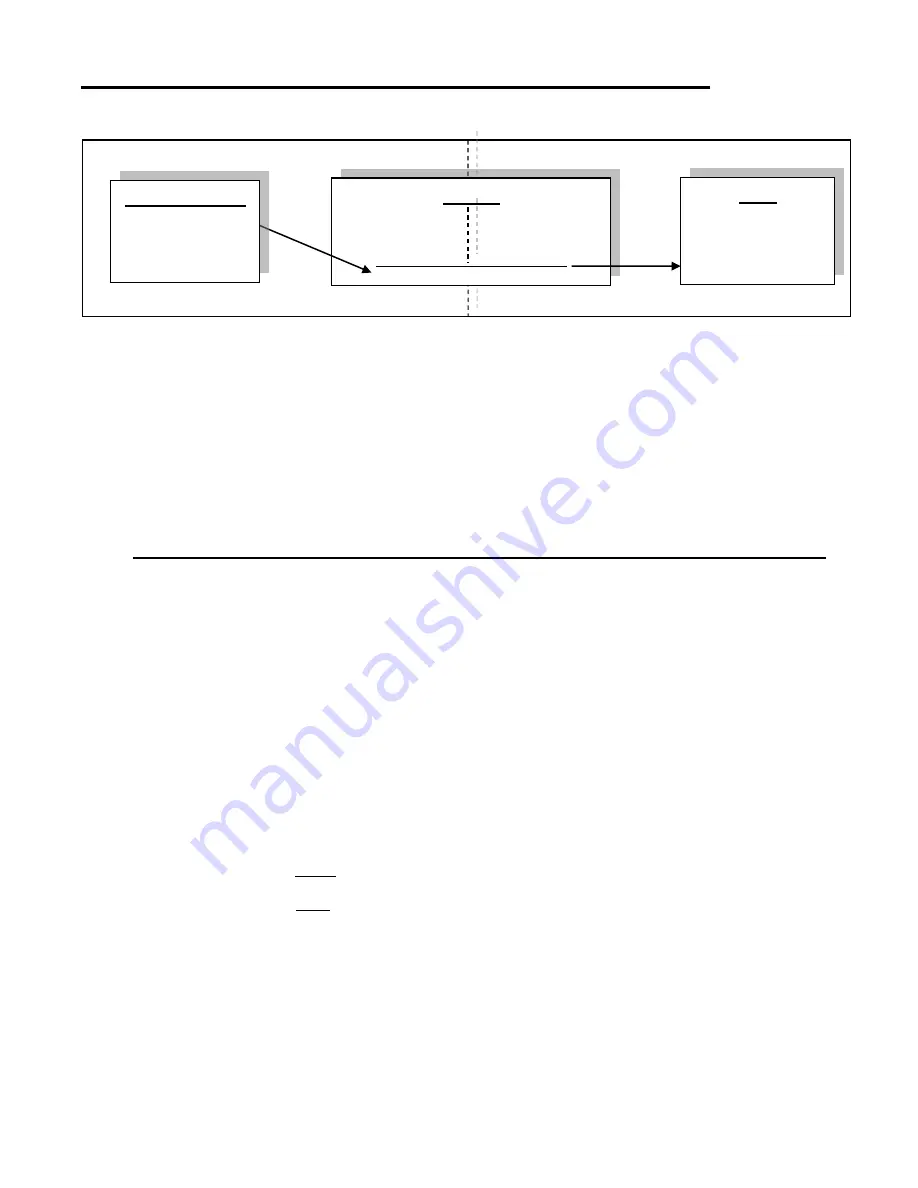
Remote Client
– This is an application on the client computer (PC, laptop, mobile phone) such as a web browser. The
client in this example is a web browser used to connect to the NVR.
Router
- Your router allows network traffic from the LAN to access data from a WAN (such as the Internet), and vice
versa. Your router has two IP addresses:
•
The WAN IP Address (also called a public, Internet, or external IP address) is the IP address assigned to your
router by your Internet service provider (Cable modem, DSL, wireless card, etc...). Use this address when
connecting to the NVR from outside your LAN.
•
The LAN IP Address (also called a private or internal IP address) is an IP address that only computers on your
Internal LAN can connect to.
NVR
– In this example, the NVR is a software program on a computer in your local network you want to access from
outside your LAN.
In order for the Remote Client to connect to the NVR, the network traffic must pass through the Router. For security
reasons, most routers do not allow public traffic to pass through and connect to devices located on your private network.
To allow this, you must enable “Port Forwarding” on your router. Consult your router manual for instructions on how to
change the Port Forwarding settings (also called Network Address Translation or NAT).
When you enable Port Forwarding on the router, the router needs to know a few things:
•
The port number to forward. This must match the listening port on the NVR. Port 80 is the default for web traffic.
(see ‘useful tips’ below)
•
The IP address of the NVR. The IP address of the NVR should be a static IP address.
•
Type of traffic (TCP and/or UDP). Choose TCP for most NVR’s and IP cameras.
Quick this steps:
1)
Assign the NVR a static IP Address. (192.168.1.51 in this example)
2)
Configure NVR to use any port number you choose. (Port 51080 in this example)
3)
Log into the router and enable port forwarding. Forward the port number (from step 2) to the IP address of the
NVR (step 1)
4)
Log into the router to determine the Public (WAN) IP address. You can also use sites like http://whatismyip.com
from the NVR PC.
5)
If connecting from outside your local network, use the Public (WAN) IP Address and Port combination to access
your NVR. In this example enter : http://66.189.8.1:51080
6)
If connecting from inside your local network, use the Private (LAN) IP Address and Port combination to access
your NVR. In this example enter : http://192.168.1.51:51080
Some useful tips:
•
Port 510
80 is the web port. You can use it, but be aware that some ISP’s block non-standard ports. Also, the
NVR may be picked up by search engines. Additionally, automated bots can attempt to break into your system.
Port values higher than 1024 are recommended.
•
You should enable password protection for the NVR.
•
If your Internet service provider does not assign you a static WAN IP address, you can use Dynamic DNS
services such as dyndns.org to monitor IP address changes. You can then use an easy name to access your
NVR, such as http://mynvr.dyndns.org:51080.
Public / Wide Area Network (WAN)
Private/ Local Area Network (LAN)
Router
66.189.8.1 192.168.1.1
WAN IP (external) LAN IP (Internal)
Public IP
Private IP
Forward port 51080 to 192.168.1.51
NVR
192.168.1.51
Static LAN IP address
Listening on port 51080
Remote Client
Web Browser
Connect to:
http://66.189.8.1:51080
















