RuralConnect® Gen3 User Manual V1.0
Page | 17 of 57
Copyright
©
2020 Carlson Wireless Technologies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Geolocation Details (Latitude/Longitude)
You must have each
unit’s geolocation in
decimal degrees
. For radios not deployed, enter the
coordinates for their storage location.
NOTE: ETSI regulations mandate these values be accurate within 30 meters. International
regulations may vary.
Antenna Height
WSDB registrations for each site include the antenna height above ground level (HAGL) in meters.
GPS-enabled units determine HAGL, with reference to the location of the GPS antenna. GPS values
are accurate within eight (8) meters
. If using GPS, you must include the difference in height between
the GPS antenna and the TVWS antenna
.
NOTE: ETSI regulations mandate the antenna height cannot exceed 30 meters AGL, nor 250
meters Height Above Average Terrain (HAAT). International regulations may vary.
3.3.2. Owner & Operator Information
Where use of a spectrum database is required, contact information is required for both the owner
and operator of the equipment. This information is used to register each radio with a White Space
Database (WSDB).
NOTE: Registration details imply explicit responsibilities and are public record.
If you own and operate the equipment, you can enter the same information for both the owner and
operator
details. You may want to specify a different “operator” contact, a lead technician that will be
responsible for the system hereon.
If your networks are operated by an organization that does not own the equipment, be sure the
owner and operator fields accurately detail the appropriate contacts.
Software Configuration
The following section is a brief overview of the steps required to configure your RuralConnect
®
system.
Most management of a RuralConnect
®
system is done via the web-based Graphical User Interface
(GUI) that runs on the Base Station. Once the equipment has been set up on your bench, you will
access the GUI via your web browser.
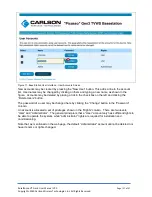
3.4.1. Finding the Base Station on Your Network
You may access the unit from your local network via an IP address or hostname.
IP Address
The local IP address of a Base Station can be static or assigned dynamically by your DHCP server.
If your unit came with a default IP address, it would include a paper and/or sticker with the address.
Otherwise, the unit is likely DHCP-enabled and you will need to determine its address.
Using the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), you can find the local IP address of a Base Station.
From a Windows PC open a command prompt and ru
n the command “arp -a”. You will see a list of
IP and MAC addresses. Look for a MAC address starting with “
70-b3-d5-17
”. You can use the
corresponding IP address to connect to the Base Station.
This ARP method only works if your computer is on the same subnet as the Base Station and both
have shared information on that network. You can download and use a “ping scanner” utility to