HY-LINE truecon Router Handbuch Seite 28
HY-LINE Systems GmbH
Inselkammerstr. 10 82008 Unterhaching systems(at)hy-line.de www.hy-line.de/systems
D
D
y
y
n
n
D
D
N
N
S
S
-
-
F
F
u
u
n
n
c
c
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
a
a
l
l
i
i
t
t
y
y
:
:
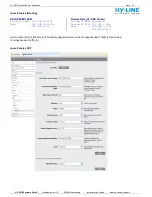
How Dynamic DNS works
Once you setup a Dynamic DNS hostname, the hostname you make will point to your new IP. You can
run an update client to keep this hostname up to date 24x7, so you never lose access, even if your IP
changes. Where you would normally need a static IP, DynDNS
®
allows you to save the additional costs of
upgrading and allows you to use your dynamic IP address. You can run your server or network device
without a problem with DynDNS
®
. DynDNS
®
users have web, email, FTP and any other kind servers you
can think of. The best part of using Dynamic DNS is you no longer have to keep memorizing your new IP
address!
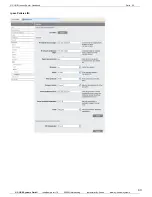
How a Dynamic DNS service affects your server
Dynamic DNS does not take up any of your server's bandwidth, since no traffic actually goes through
them. Any user trying to reach your device will send out an initial DNS query to the DNS provider to get
your IP address then after that the traffic goes directly to you. This means there is no increase in latency,
nor is there any restriction on how the connection can be used, beyond those placed on you by your ISP.
Can a Dynamic DNS service replace my static IP?
In most situations a static IP is not required. The Dynamic DNS service allows your host to be mapped to
your IP, even when your IP changes. However, there can be some issues depending on your situation,
some of which are outlined below:
1) If your IP changes while you are connected to your server, you may lose the connection and will need
to reconnect.
2) While most software and hardware will work with a hostname, some older equipment requires an IP
and will not work with a hostname. In those situations a Dynamic DNS service won't help.
3) Many email providers block mail from servers that have dynamic IP addresses. To get around this
issue you would need to use an outbound mail relaying service to allow you to send out mail through their
servers, such as MailHop Outbound.
4) Many satellite ISPs place users behind a NAT, which means they do not have a publicly accessible IP;
unfortunately this prevents them from running any kind of server.
5) You can not setup Reverse DNS using a dynamic IP, only a static IP. This is because your IP is
actually owned and controlled by your ISP. In the event you need Reverse DNS to send mail you should
upgrade to a static IP address or send mail using a SMTP smart host, such as MailHop Outbound.